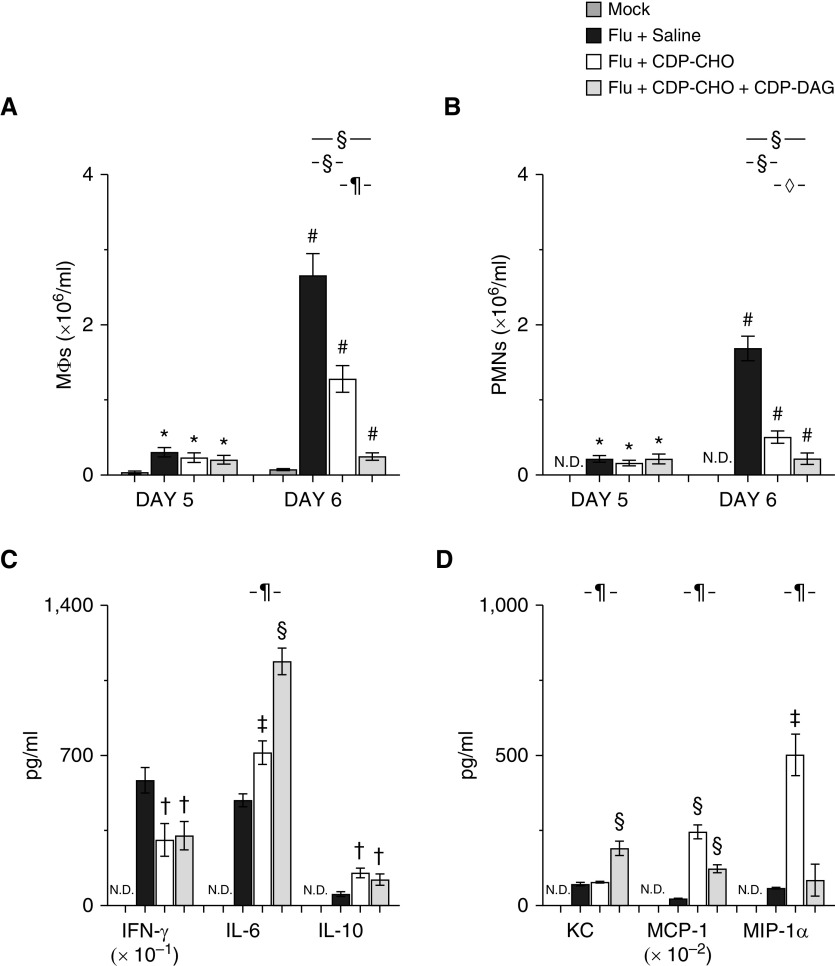
Figure 4.
Liponucleotide PEP has antiinflammatory effects in IAV-infected mice. Effect of treating mice infected with H1N1 influenza A/WSN/33 (10,000 pfu/mouse) with sterile 0.9% saline (50 μl/mouse, i.p.), 100 μg/mouse CDP-CHO (in 50 μl sterile 0.9% saline i.p.), or 100 μg/mouse CDP-CHO + 10 μg/mouse CDP-DAG (in 50 μl sterile 0.9% saline i.p.) daily on (A) BAL fluid (BALF) MΦs (×106/ml; n ≥ 10/group) at 5 and 6 d.p.i., (B) BALF PMNs (×106/ml; n ≥ 10/group) at 5 and 6 d.p.i., (C) BALF cytokines (IFN-γ [pg/ml × 10–1], IL-6 [pg/ml], and IL-10 [pg/ml]) (n ≥ 5/group) at 6 d.p.i., and (D) BALF chemokines (KC/CXCL-1 [pg/ml], MCP-1.CCL-2 [macrophage chemotactic protein-1; pg/ml × 10–2], and MIP-1α/CCL-3 [macrophage inflammatory protein-1α; pg/ml]) (n ≥ 5/group) at 6 d.p.i. All cytokines and chemokines were below the limits of detection in BALF from mock-inoculated mice. All data were analyzed by ANOVA with a Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison post hoc test and are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 and #P < 0.001 versus mock-inoculated mice. †P < 0.05, ‡P < 0.005, and §P < 0.001 versus saline-treated, IAV-infected mice. ◊P < 0.05 and ¶P < 0.001 versus CDP-CHO–treated, IAV-infected mice. MΦ = macrophage; MCP-1 = monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MIP-1α = macrophage inflammatory protein-1α; N.D. = none detected; PMN = neutrophil.