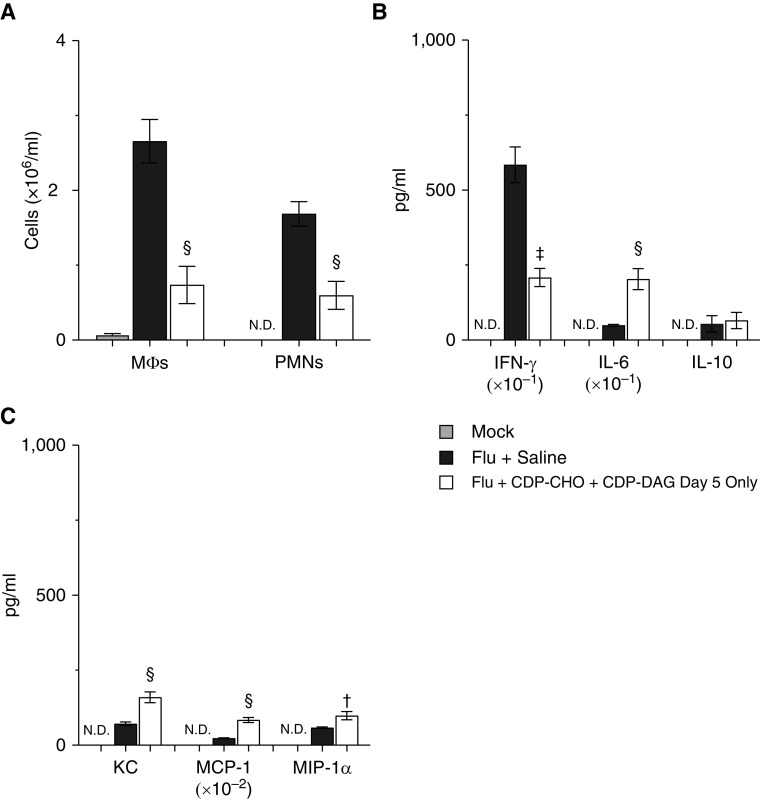
Figure 7.
Single-dose LPN treatment reduces pulmonary inflammation in mice with severe IAV-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Effect of treating mice infected with H1N1 influenza A/WSN/33 (10,000 pfu/mouse) with 100 μg/mouse CDP-CHO + 10 μg/mouse CDP-DAG (both i.p.) at 5 d.p.i. only on 6 d.p.i. values for (A) BALF MΦs (×106/ml; n ≥ 6/group) and PMNs (×106/ml; n ≥ 6/group), (B) BALF cytokines (IFN-γ [pg/ml × 10–1], IL-6 [pg/ml], and IL-10; [pg/ml]) (n ≥ 5/group), and (C) BALF chemokines (KC/CXCL-1 [pg/ml], MCP-1/CCL-2 [pg/ml × 10–2], and MIP-1α/CCL-3 [pg/ml]) (n ≥ 5/group). All cytokines and chemokines were below the limits of detection in BALF from M. All data were analyzed by ANOVA with a Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison post hoc test and are presented as mean ± SEM. †P < 0.05, ‡P < 0.005, and §P < 0.001 versus F+S mice at 6 d.p.i.