Fig 1. ROCK2 controls the balance between pro-inflammatory and Treg cell subsets, regulates cytoskeletal dynamics and profibrotic gene expression and drives both chronic inflammation and fibrosis in cGVHD.
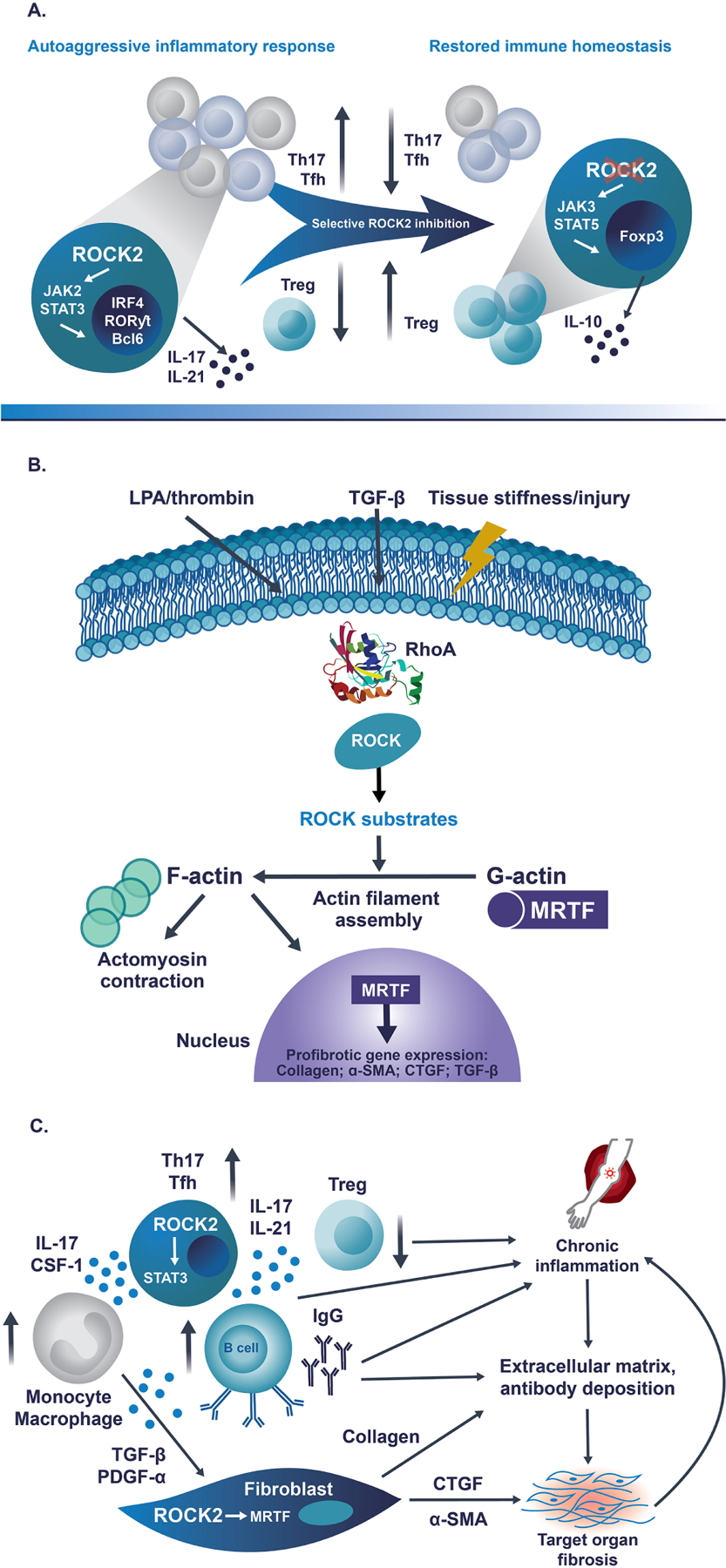
A) During pro-inflammatory immune response, ROCK2 specifically interacts with phosphorylated STAT3. ROCK2 activity is required for the formation of the JAK2/STAT3 complex in Th17 and Tfh cells. Therefore, ROCK2 inhibition results in decreased activation of STAT3 and other Th17/Tfh transcription factors, including IRF4, RORγT and Bcl6, triggering the significant downregulation of both Th17 and Tfh cells. In addition, selective ROCK2 inhibition promotes interaction of ROCK2 with JAK3, leading to the increased phosphorylation of STAT5, the upregulation of Treg cells and the restoration of immune homeostasis. B) Extracellular mediators, such as LPA, thrombin and TGF-β, as well as mechanotransduction forces, activate the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway and its numerous downstream substrates. This results in the polymerization of G-actin to F-actin and the formation of contractile fibers. ROCK-induced actin polymerization frees the transcription factor MRTF, which is normally sequestered in cytoplasm, to translocate to the nucleus and initiate transcription of several profibrotic genes, including collagen, α-SMA, CTGF and TGF-β, resulting in changes to the cellular structure and an increase in tissue stiffness. C) ROCK2 promotes the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-17 and IL-21 via STAT3 phosphorylation, consequently leading to the imbalanced activation of B cells and monocytes/macrophages, which results in the excessive production of autoantibodies and the secretion of profibrotic factors, respectively. The pro-inflammatory milieu downregulates the number and function of immunosuppressive Treg cells to sustain the chronic inflammation. In addition, ROCK2 facilitates MRTF-mediated transcription and increased expression of smooth muscle actin and CTGF, stimulating the differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and the increased production of collagen, which promote the development of fibrosis in target organs. Thus, ROCK2 is integral in the cross-talk between the inflammatory and the fibrotic processes driving the pathology of cGVHD.
α-SMA, alpha smooth muscle actin; Bcl6, B-cell lymphoma 6; cGVHD, chronic graft-versus-host disease; CSF-1, colony-stimulating factor-1; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; Foxp3, forkhead box P3; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IL-10, interleukin 10; IL-17, interleukin 17; IL-21, interleukin 21; IRF4, interferon regulatory factor 4; JAK2, Janus-associated kinase 2; JAK3, Janus-associated kinase 3; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; MRTF, myocardin-related transcription factor; PDGF-α, platelet-derived growth factor α; ROCK2, rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase-2; RORγt, retinoic-acid-receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor γ; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; Tfh, follicular helper T [cell]; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; Th17, type 17 helper T [cell]; Treg, regulatory T [cell].
