Figure 4.
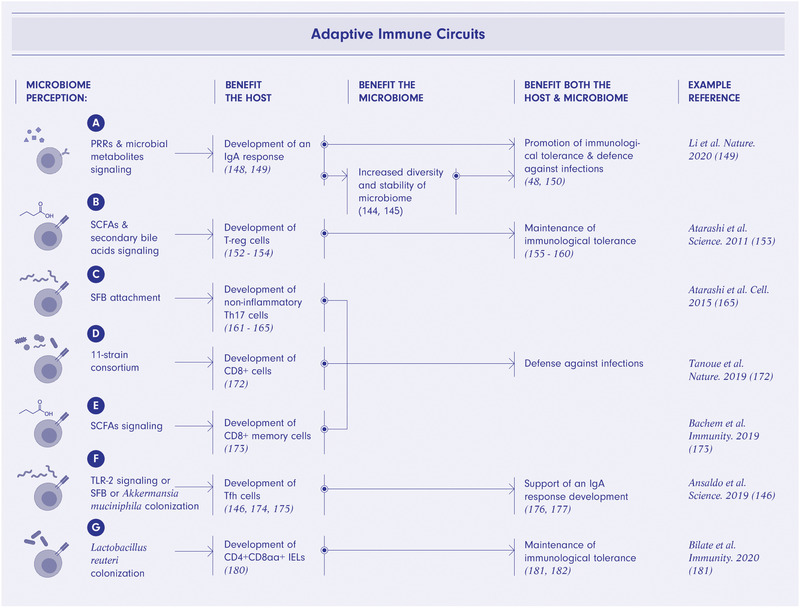
T and B cell‐microbiome mutually beneficial interactions. Microbial sensing via pattern recognition receptors signaling and microbial metabolites signaling promotes an IgA humoral response curating microbiome diversity, promoting immunological tolerance, and providing defense against infections (A). Short‐chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and secondary bile acids signaling promote differentiation of T regulatory cells ultimately bolstering immunological tolerance toward microbiome (B). Specific bacterial species such as segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB) or the 11‐strain consortium and SCFA signaling result in differentiation of Th17 (C), CD8+, (D) and memory CD8+ cells (E) respectively and provide defense of the host and microbiome from infections. TLR2 signaling or SFB or Akkermansia muciniphila colonization promotes the differentiation of Tfh cells that support development of an IgA response thus curating microbiome composition and benefiting the host and microbiome (F). Lactobacillus reuteri colonization promotes differentiation of tolerogenic CD4+CD8αα+ intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) thus enhancing immunological tolerance towards microbiome (G). The figure was created using BioRender.com.
