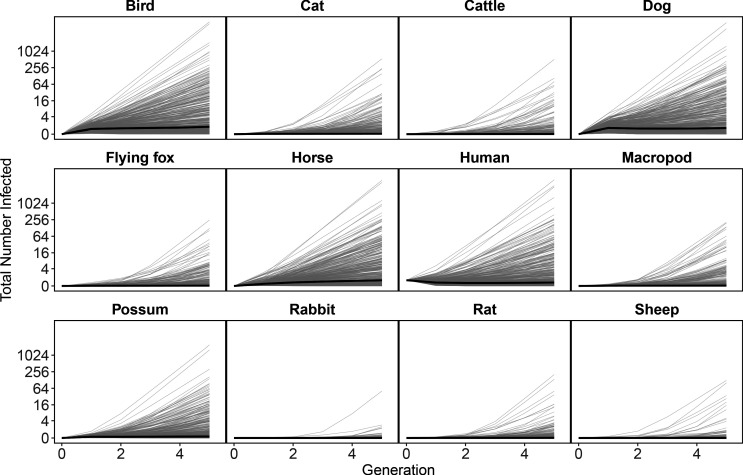
Appendix 2—figure 5. An initial human infection propagates infection through the host community.
Starting with a single infected human in generation ‘zero’ (all hosts begin with zero infected individuals except humans), the next generation matrix approach can be used to approximate (using the time step of a generation) how an epidemic would unfold in the community. Here, we show the total number of new infections of each species as the infection spreads in the community across generations beginning with the source infection in one human. In generation one, all infections arise from the source human infection. In subsequent generations, the plotted number of infections for each species is the estimated total number of infections in that species arising from all transmission pathways. Our median estimate for Ross River virus transmission in Brisbane is just above one, which results in a very slow increase in cases over generations (solid lines); however, large uncertainty for the number of infections produced by each infected host and mosquito (see Figure 2, Figure 3) results in the possibility of explosive epidemics and thousands of infected individual hosts after a few generations. The thin grey black lines are 500 epidemic realizations. Because we assume a fully susceptible host and vector population, this is an epidemic simulation, which would over-estimate the amount of RRV transmission in Brisbane because of the high host immunity in the host population that is ignored here.