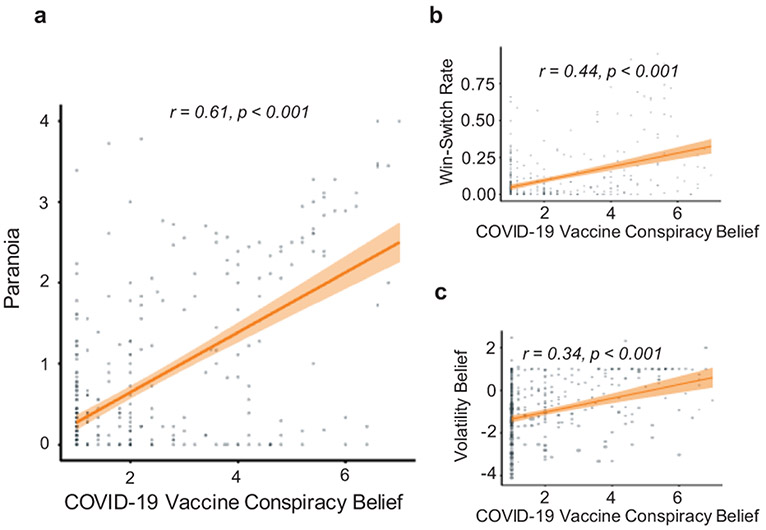
Figure 7. Relating vaccine conspiracy beliefs to paranoia and task behaviour.
We assayed individual’s (N=403) COVID-19 vaccine conspiracy beliefs to investigate underlying relationships to behaviour. a, We find individuals with higher paranoia endorse more vaccine conspiracies (r=0.61, p<0.001). b, COVID conspiracy beliefs were correlated with erratic task behaviour (r=0.44, p<0.001), and c, perturbed volatility priors (r=0.34, p<0.001). Analysis performed on individuals who responded to covid vaccine conspiracy questions.