Fig. 1. Loss of Rad27 causes increased levels of Pms1 foci.
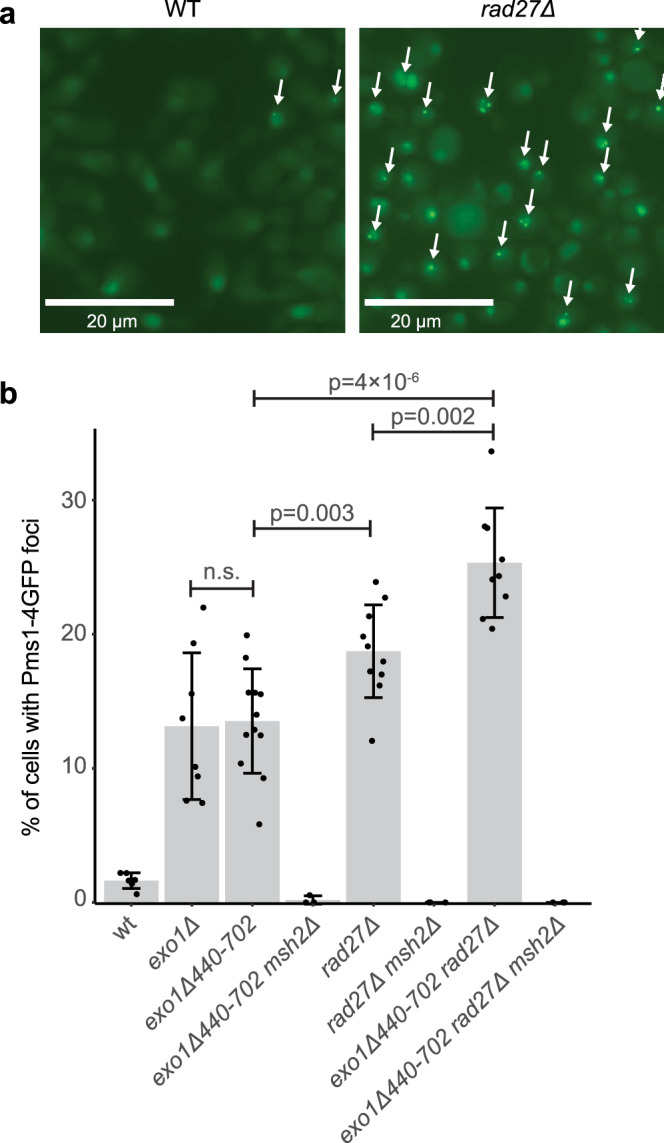
a Example fluorescence micrographs of wild-type and rad27Δ cells expressing Pms1-4GFP show increased levels of foci (white arrows) in the rad27Δ cells. The bar indicates 20 μm. b Quantitation of the average number of Pms1-4GFP foci; error bars represent the standard deviation, the bars indicate the mean of the observations, and the points show the results from each field quantified. The statistical test used was a two-tailed t-test. Deletion of EXO1 or the exo1Δ440-702 truncation cause equivalent levels of Msh2-dependent Pms1-4GFP foci. Deletion of RAD27 causes higher levels of Msh2-dependent of Pms1-4GFP foci than the exo1Δ440-702 truncation, and the exo1Δ440-702 rad27Δ double mutant strain has higher levels of Msh2-dependent Pms1-4GFP foci than either single mutant. The reported experiments were done twice and a minimum of 8 independent fields were captured and quantified per strain analyzed.
