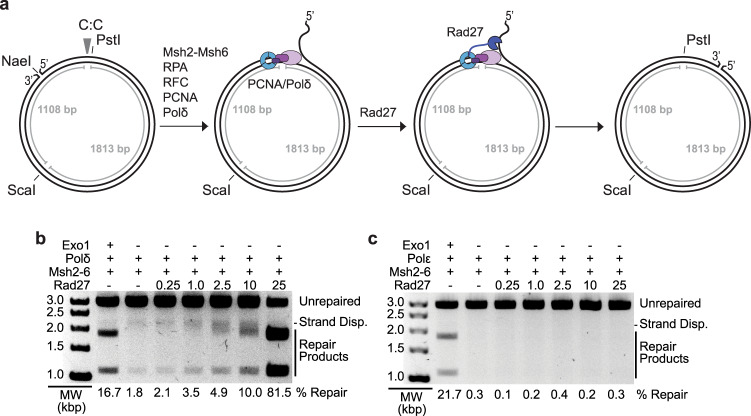
Fig. 2. Reconstitution of 5′ nick-directed Rad27-dependent MMR using the NaeI-nicked CC substrate.
a Schematic representation of the DNA substrate for the reconstituted repair assays. The substrate has a nick at the NaeI site and the CC mispair, indicated by the arrowhead, disrupts the PstI site. Recruitment of PCNA and DNA polymerase δ to the NaeI nick leads to strand-displacement synthesis and formation of a 5’ flap which is cleaved by Rad27. Incomplete flap cleavage gives rise to slower migrating product bands. b, c Assays of 5′ nick-directed repair of the CC substrate, in which different proteins were omitted or substituted as indicated, using either polymerase δ b or polymerase ε c. Amounts in pmole of Rad27 used are indicated for each lane. All reactions also contained PCNA, RFC-Δ1N, and RPA. Other than Rad27, the amounts of all proteins used in the assays are as listed in the “Methods” section. MW, molecular weight markers. The percent repair corresponds to the fraction of all DNA in each individual lane susceptible to PstI cleavage, including those labeled “strand displacement” and “repair products”. A minimum of three independent experiments was performed.