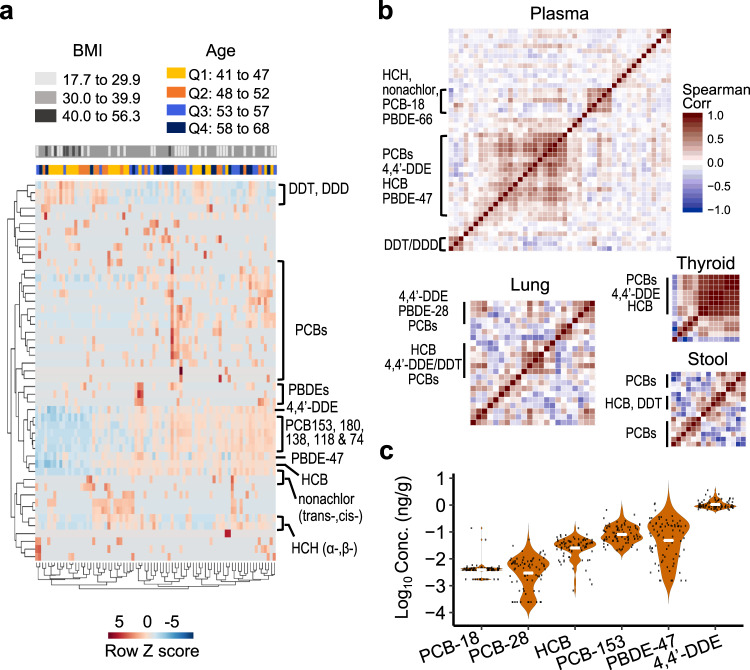
Fig. 4. XLE with GC–HRMS supports detection and quantification of environmental chemicals in different biologic materials.
a Human plasma from 80 individuals without known occupational or environmental exposures of concern was analyzed for 49 chemicals and visualized by unsupervised two-way hierarchical clustering of log-transformed intensities. Subjects were color-coded into three body mass index (BMI) groups and age quantiles (Q1–Q4). The results show that high-throughput analysis of environmental chemicals enables study of relationships of chemical distributions and associations with health characteristics. b XLE supports quantification of environmental chemicals in human plasma (n = 80 biologically independent samples), lung (n = 11 biologically independent samples), thyroid (n = 5 biologically independent samples), and stool (n = 6 biologically independent samples) samples. Hierarchical cluster analysis of Spearman’s correlation among quantified environmental chemicals shows co-exposure of different chemical classes and illustrates that XLE supports quantification of multiple classes of chemicals in different tissue types for integrative analyses of diverse chemical exposures. c Concentrations and distribution of chemicals prevalent in plasma (n = 80 biologically independent samples) samples shows that XLE is suitable to support quantification in human plasma (white bar—median; black dot—individual sample concentration). DDD dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane, DDT dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, DDE dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene, HCB hexachlorobenzene, HCH hexachlorocyclohexane, PBDE polybrominated diphenyl ethers, PCB polychlorinated biphenyls. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.