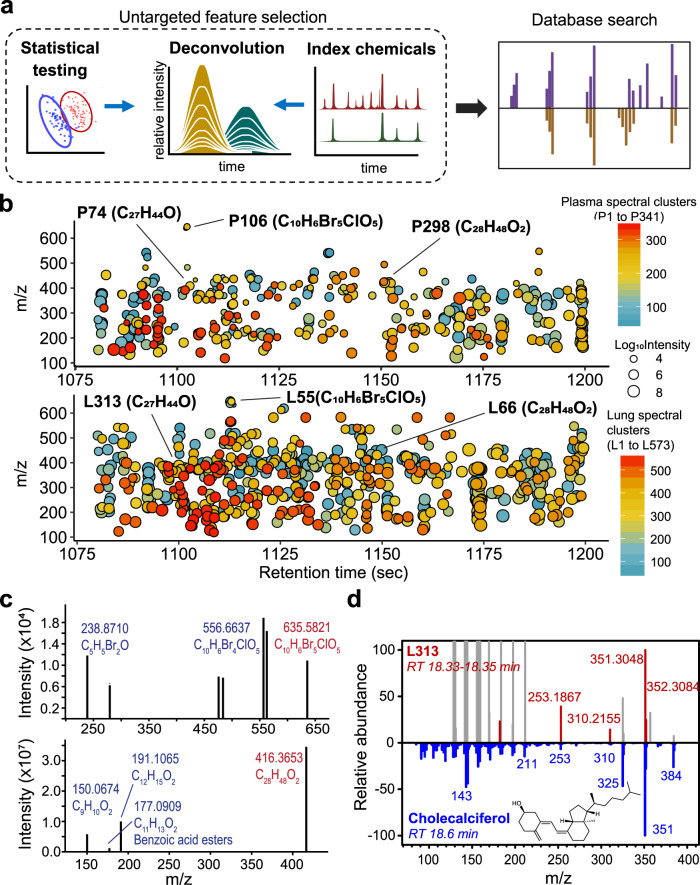
Fig. 5. XLE with GC–HRMS measures unidentified environmental chemicals to support exposome epidemiology.
a Data from untargeted analyses can be used directly for biostatistical and bioinformatics analyses of relationships to health markers without chemical identification. For instance, in untargeted feature selection, principal component (PC) analysis can select chemical features that discriminate sample groups (left: red and blue), while chromatographic retention index relative to known index chemicals (right: dark green), can inform properties of selected features. Deconvolution defines the accurate mass spectral signals (middle: golden), which along with retention time and ion intensity, can be incorporated into exposome reference databases and used for subsequent investigation, such as database searches (purple: library spectra; golden: experimental spectra). b Application of tools such as RAMclustR28 to untargeted data allows co-eluting m/z features to be studied as possible products derived from an unidentified chemical. In this example of an analysis of human plasma (n = 60 biologically independent samples) and lung (n = 11 biologically independent samples), unidentified signals of a two-minute retention-time interval are clustered into spectra and color-coded based on clusters. Size of circles reflects weighted intensity calculated based on compiled spectra28. c Clustered m/z spectra are likely to include unidentified environmental chemicals and can be used for discovery of unidentified chemical structures. Examples are presented showing putative molecule formula assigned to spectra by MS-Finder ver 3.4230. Candidates with the highest formula scores (P106: 2.4; P208: 4.3) in MS-Finder were selected. Blue—putative fragment ion; Red—putative precursor ion. d One spectral cluster (L313: red) was confirmed by library search of spectra (blue) and retention-time match with authentic standard (Supplementary Fig. 4) showing that XLE supports identification of chemicals using an untargeted approach. Missing spectral matches were identified at the same retention time (gray) and were not clustered with L313 by RAMclustR due to low-intensity correlations. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.