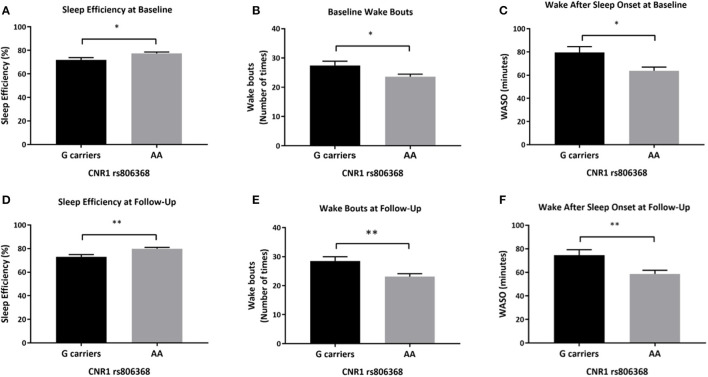
Figure 3.
Differences in actigraphy-based sleep quality measures by CNR1 rs806368 genotype at baseline and follow-up. This figure demonstrates that at based on actigraphy-based measures, both at baseline (A–C) and follow-up (D–F), G carriers of CNR1 rs806368 genotype had poorer sleep efficiency, more wake bouts and more wake minutes after sleep onset after controlling for age, sex, years of education, pack years, Alcohol Dependence Severity (ADS) scores, Ancestry-informative marker (AIM scores for Africa, Europe), presence of mood disorders, and/or anxiety disorders, presence of Cannabis Use Disorder, and/or any Substance Use Disorder other than nicotine. (A) Baseline Sleep Efficiency: [F(1,89) = 5.324, p = 0.023, N = 101], (B) Baseline wake bouts: [F(1,89) = 4.952, p = 0.029, N = 101], (C) Baseline WASO: [F(1,89) = 6.174, p = 0.015, N = 101], (D) Follow-up Sleep Efficiency F(1, 65) = 9.052, p = 0.004, (E) Follow-up wake bouts: [F(1, 65) = 8.125, p = 0.006], (F) Follow-up WASO: [F(1, 65) = 7.677, p = 0.007]. Bars represent adjusted means and error bars denote standard errors. WASO, Wake After Sleep Onset. *p <0.05, **p <0.01 and Bonferroni adjusted.