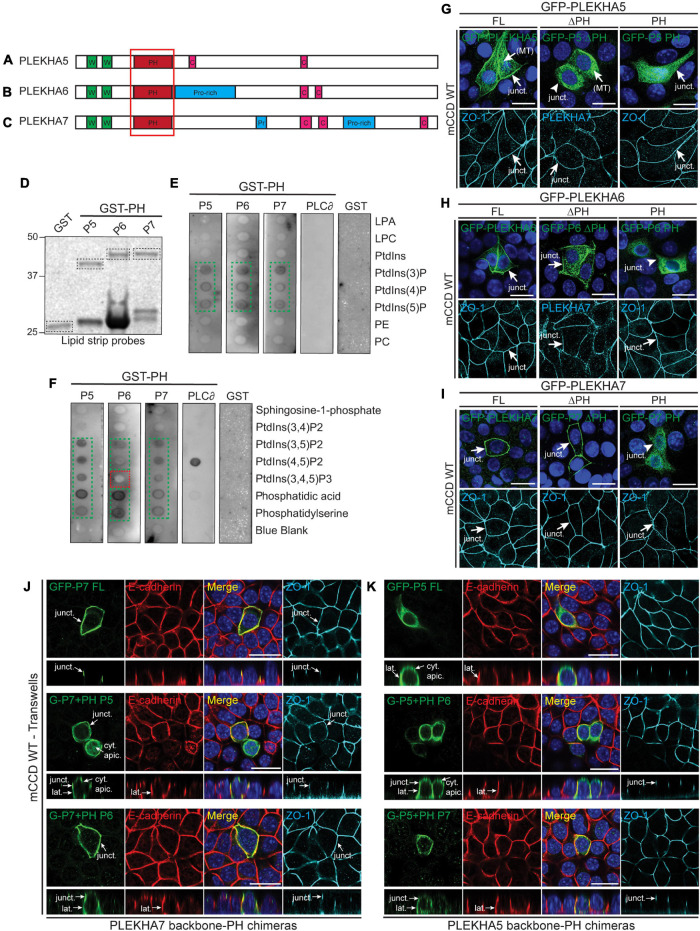
FIGURE 4.
Phospholipid binding and cellular localizations of the PH domains of WW-PLEKHAs. (A–C) Scheme of the structural organization of PLEKHA5 (A), PLEKHA6 (B), and PLEKHA7 (C) showing the domains: WW (Trp-Trp) (W) in green, PH (pleckstrin homology) in red, Proline-rich (Pro-rich or Pr) in blue, coiled-coil (C) in pink. Red box indicates the structural domain analyzed. (D–F) In vitro interaction of PH domains of WW-PLEKHAs with phospholipids. Coomassie staining (D) of purified GST fusions of PH domains of PLEKHA5 (P5), PLEKHA6 (P6) and PLEKHA7 (P7) (framed bands), and (E,F) IB analysis of lipid-protein overlay assay (GST-PH domain of phospholipase C-∂1 (PLC∂) as positive control, GST alone as negative control). Green frames highlight binding, red frames indicate low/undetectable interaction. LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; PtdIns, phosphatidylinositol; P, phosphate; P2, biphosphate; P3, triphosphate; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine. (G–I) IF analysis of the localization of exogenous GFP-tagged constructs of PLEKHA5 (G), PLEKHA6 (H), and PLEKHA7 (I) in WT mCCD cells. Either full-length (FL), or FL with a deletion of the PH domain (ΔPH), or PH domain alone (PH) were used. ZO-1 and PLEKHA7 are used as junctional markers. Junctional (junct.) and fibrillar microtubules-like [(MT)] localizations are indicated. Arrows show labeling, arrowheads indicate low/undetectable labeling. (J,K) IF analysis of the localization of either GFP-tagged PLEKHA7 (P7) (J) or PLEKHA5 (P5) (K) constructs in WT mCCD cells. Either full-length (FL) proteins, or chimeras where the PH domain was replaced [either from P5 or P6 in PLEKHA7 (J), or from P6 or P7 for PLEKHA5 (K)] are shown. mCCD cells were polarized on transwells and XZ section were taken at the horizontal middle of the XY plane (square panels). Cytoplasmic sub-apical (cyt. apic.), junctional (junct.), and lateral (lat.) localizations are indicated. E-cadherin and ZO-1 are used as lateral and junctional markers, respectively. Scale bar = 20 μm.