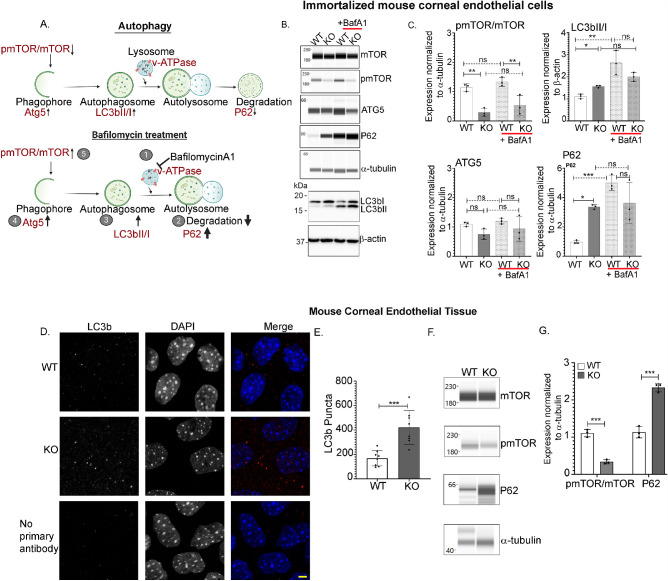
Figure 1.
Autophagy flux is aberrant in Slc4a11 KO corneal endothelial cells. (A) In basal autophagy, autophagosome formation occurs followed by fusion with lysosomes and the degradation of substrates. In BafilomycinA1 (BafA1) treated cells (1), the lysosomal proton pump (v-ATPase), which is responsible for its acidic environment is inactivated. This leads to the accumulation of non-degraded autophagy substrates in the cell (2), which further increases the levels of proteins involved in autophagosome (3), and phagophore formation (4), which eventually increases pmTOR/mTOR ratio (5). (B) Wes immunoassay for p-mTOR (Ser 2448), mTOR, Atg5, P62 in Slc4a11 WT and KO MCEC (± 50 nM BafA1). Western Blot of the same lysates were probed for LC3b and β-actin. (C) Quantification of panel B data, mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ns = not significant (1-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). (D) Immunofluorescence of corneal endothelial tissue from Slc4a11 WT and KO mice for LC3b (red) counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar – 5 µm. (E) Quantification of LC3b puncta from panel D data, mean ± SD, ***P < 0.001 (Student's t-test). (F) Wes immunoassay of mTOR, pmTOR (Ser 2448) and P62 from Slc4a11 WT and KO corneal endothelial tissues. (G) Quantification of data from panel F, mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001 (Student's t-test, n = 3).