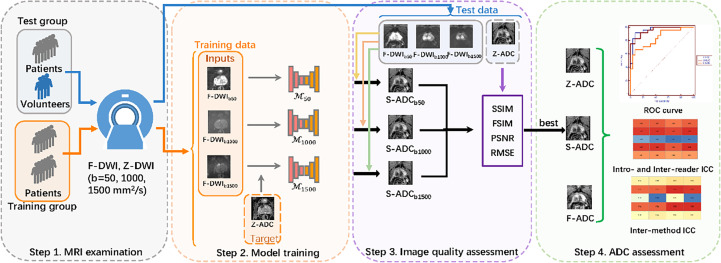
Figure 1.
Overall study flow diagram. Step 1: All the patients and healthy volunteers underwent multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the prostate, including full field-of-view (FOV) diffusion-weighted imaging (f-DWI) and zoomed FOV diffusion-weighted imaging with b-values of 50, 1,000, and 1,500 s/mm2. Step 2: The models that used full f-DWI with different b-values (f-DWIb50, f-DWIb1000, and f-DWIb1500) to synthesize the apparent diffusion coefficient (s-ADC) maps (s-ADCb50, s-ADCb1000, and s-ADCb1500) were trained. Step 3: The image quality of s-ADCb50, s-ADCb1000, and s-ADCb1500 were evaluated using the peak signal-to-noise ratio, root mean square error, structural similarity, and feature similarity. Step 4: An ADC assessment was performed to determine reproducibility, tumor detection, and classification.