Figure 1. Associations of Cumulative Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C), Time-Weighted Average (TWA) LDL-C, and LDL-C Slope During Young Adulthood and Middle Age With Incident Coronary Heart Disease (CHD).
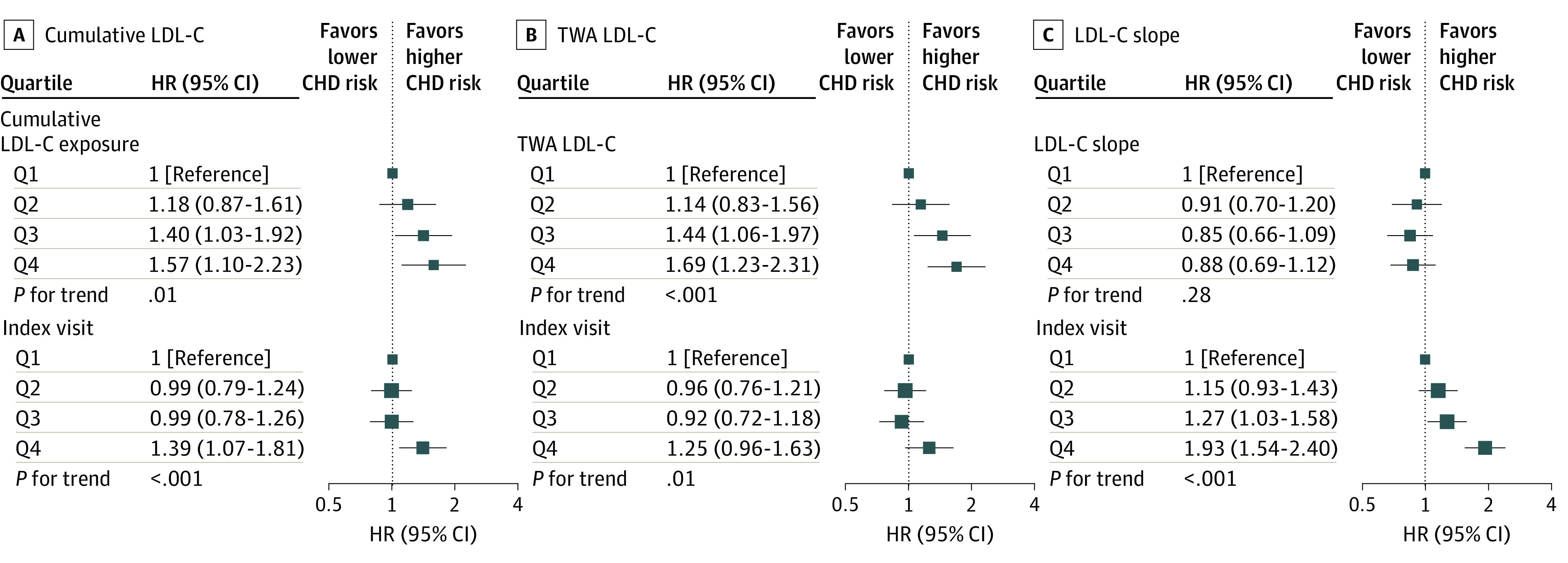
Models were stratified by study cohort and adjusted for race and ethnicity, sex, birth year, body mass index, smoking status, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, diabetes status, use of lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications, and LDL-C levels at the index visit. HR indicates hazard ratio; Q, quartile.
