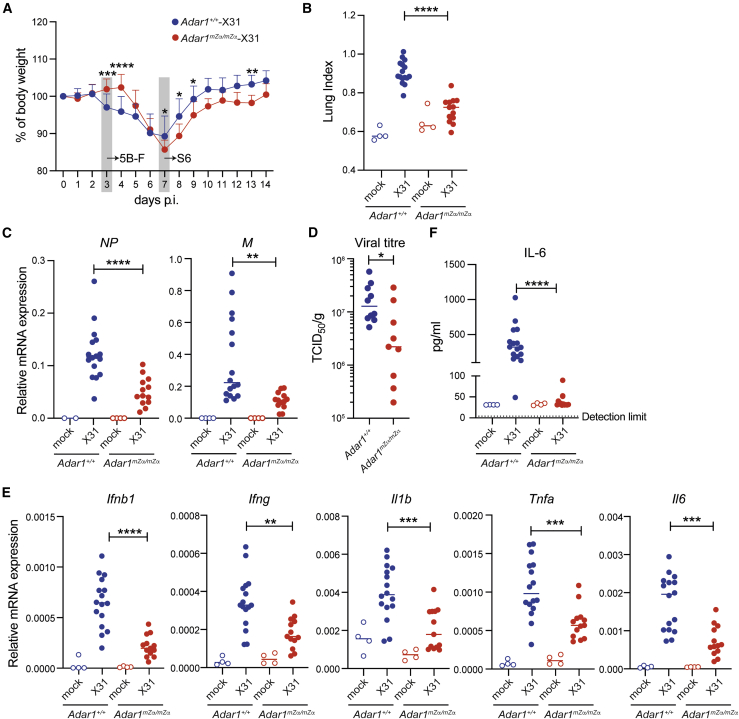
Figure 5.
Adar1mZα/mZα mice are protected from early IAV infection
(A) WT or Adar1mZα/mZα mice were infected intranasally with 0.04 HAU of IAV strain A/X-31. Body weight was monitored daily and is shown as a percentage of starting body weight.
(B–F) WT or Adar1mZα/mZα mice were infected as in (A) or mock-infected using viral growth medium. On day 3 post-infection, lungs and sera were collected. (B) A “lung index” was calculated (lung weight/body weight × 100). (C) Levels of the viral NP and M transcripts were analyzed using qRT-PCR in RNA samples extracted from total lung. Data are shown relative to Actb (NP) or Gapdh (M). (D) Lung viral titers were determined in samples from infected animals by TCID50 analysis and were normalized to lung weight. (E) Levels of the indicated mRNAs were determined as in (C). (F) Serum IL-6 concentrations were analyzed using ELISA.
In (A), data from three independent experiments including a total of 15 mice per genotype were pooled (mean + SD; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, mixed-effects analysis). In (B)–(F), pooled data from two independent experiments (mock infected, n = 4 mice per genotype; A/X-31-infected, n = 10–16 WT and n = 9–13 Adar1mZα/mZα mice) are shown. Each dot represents an individual mouse and the mean is indicated (∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, unpaired t test). See also Figure S6.