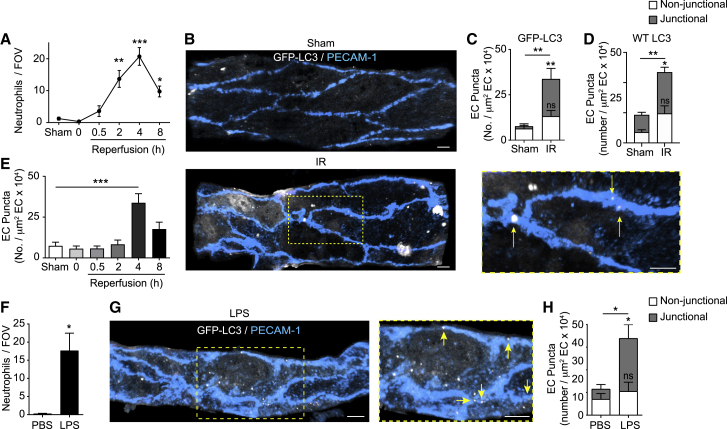
Figure 1.
Acutely inflamed microvascular ECs exhibit induction of autophagy within vascular junctions
(A–E) GFP-Map1lc3aTG/+ or WT mice were subjected to local IR injury
(A) Neutrophil extravasation at the indicated times post reperfusion, (n = 3–6 mice/group).
(B–E) Representative confocal images (n = 6) of postcapillary venules (PCVs, PECAM-1), with arrows indicating EC junctional localization of GFP-LC3 puncta (scale bar, 5 μm) (B) and quantification of (C) GFP-LC3 puncta or (D) endogenous LC3 puncta per venular EC area at 4 h and (E) at the indicated times postreperfusion (n = 3–6 mice/group).
(F–H) GFP-Map1lc3TG/+ mice were treated intrascrotally (i.s.) with PBS or LPS.
(F and G) Neutrophil extravasation (n = 3 mice/group) (F) and (G) representative (n = 3) confocal images of cremasteric PCVs (PECAM-1), with arrows indicating EC junctional localization of GFP-LC3 puncta (scale bar, 5 μm).
(H) Quantification of GFP-LC3 puncta per venular EC area (n = 3 mice/group). Dashed boxes delineate magnified areas.
Means ± SEMs. Statistically significant difference from controls or between indicated groups is shown by ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns, not significant.
See also Figure S1.