FIGURE 2.
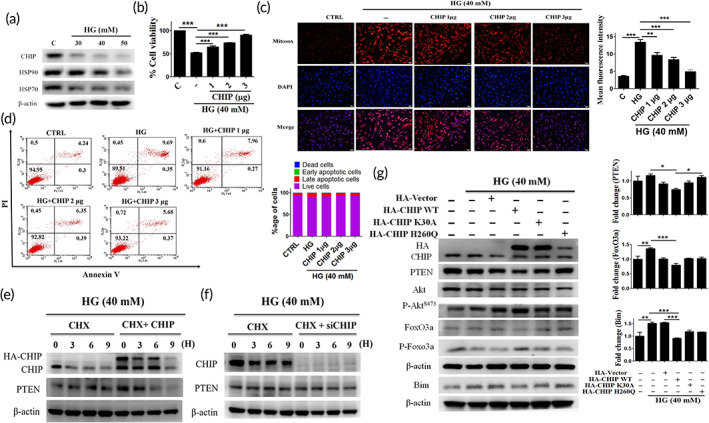
CHIP overexpressed WJMSCs attenuate hyperglycemia‐induced PTEN mediated apoptosis and oxidative stress. (a) WJMSCs were challenged with increasing concentrations of HG for 24 h, and subsequently the expression level of the chaperone system (HSP70, HSP90, and CHIP) was measured using Western blotting. (b) WJMSCs were transfected with varying increasing concentration of CHIP (1, 2, and 3 μg) followed by HG incubation for 24 h. The cell viability was detected. (C, D) WJMSCs were transfected with HA‐CHIP in the presence of HG (40 mM) for 24 h, and the mitochondrial ROS accumulation as well as apoptotic cell death were assessed using MitoSOX staining and flow cytometry. (e, f) WJMSCs were transfected with either HA‐CHIP (3 μg) or siCHIP (30 nM) for 24 h in the presence of CHX (50 μg/ml) for indicated time points were subjected to HG challenge for 24 h, and the protein expression was measured using Western blot analysis. (g) WJMSCs were transfected with pRK5‐HA‐vector (3 μg), pRK5‐HA‐CHIP (3 μg), pRK5‐HA‐K30A (3 μg), and pRK5‐HA‐H260Q (3 μg), followed by HG incubation for 24 h. Cell lysates were immunoblotted to analyze the expression of PTEN and the downstream signaling cascade. β‐actin act as a loading control. The scale bar indicates 100 μm. Values shown are means ± SD and quantification of the results shown as n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 indicates the significant difference. CHIP, carboxyl terminus of Hsc70 interacting protein; HG, high glucose; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; ROS, reactive oxygen species; WJMSCs, Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells
