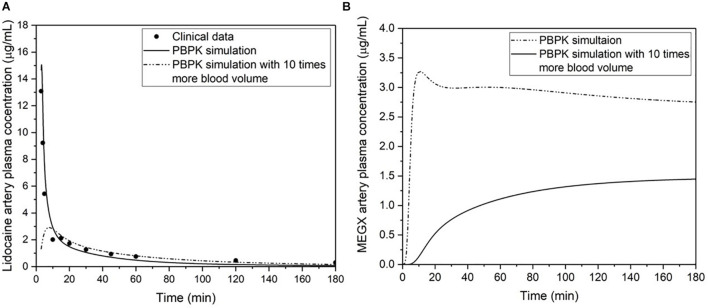
FIGURE 5.
(A) The PBPK simulation and clinical data of lidocaine artery plasma concentration change over time after an intravenous administration of 3 mg/kg body weight (Tucker and Boas, 1971). (B) Comparison of two simulations for the artery plasma concentration change of monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX, a metabolite of lidocaine) after an intravenous administration of 3 mg/kg body weight, and using published parameters for MEGX unbound fraction (Feely and Grimm, 1991), partition coefficient (Dillane and Finucane, 2010), and in vitro liver kinetics (Bargetzi et al., 1989). One simulation is modeled with physiological parameters, and the other is modeled with 10 times more blood volume while keeping all the other parameters equal and at physiological values.