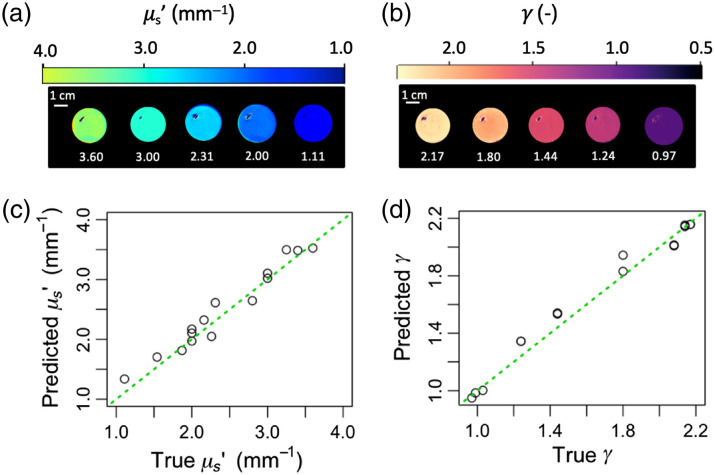
Fig. 3.
Performance of the neural network across five homogeneous phantoms with known optical properties and three wavelengths. Image cubes comprising 26 sd-SFDI images were transformed into optical property heatmaps for each phantom at each wavelength using the trained deep learning model, resulting in 15 heatmaps. (a), (b) Select heatmaps and select heatmaps, respectively, from the results, with the true value for the phantoms written in white underneath. Note these selections span multiple wavelengths and phantoms. The model accurately produces wide-field optical property heatmaps over the range of values tested. (c), (d) The accuracy of the model when run on an average spectrum from each of the phantom image cubes, where the axis is the true optical property, the axis is the predicted optical property, and the dotted green line represents unity. The mean absolute relative error was 6.8% for and 3.6% for .