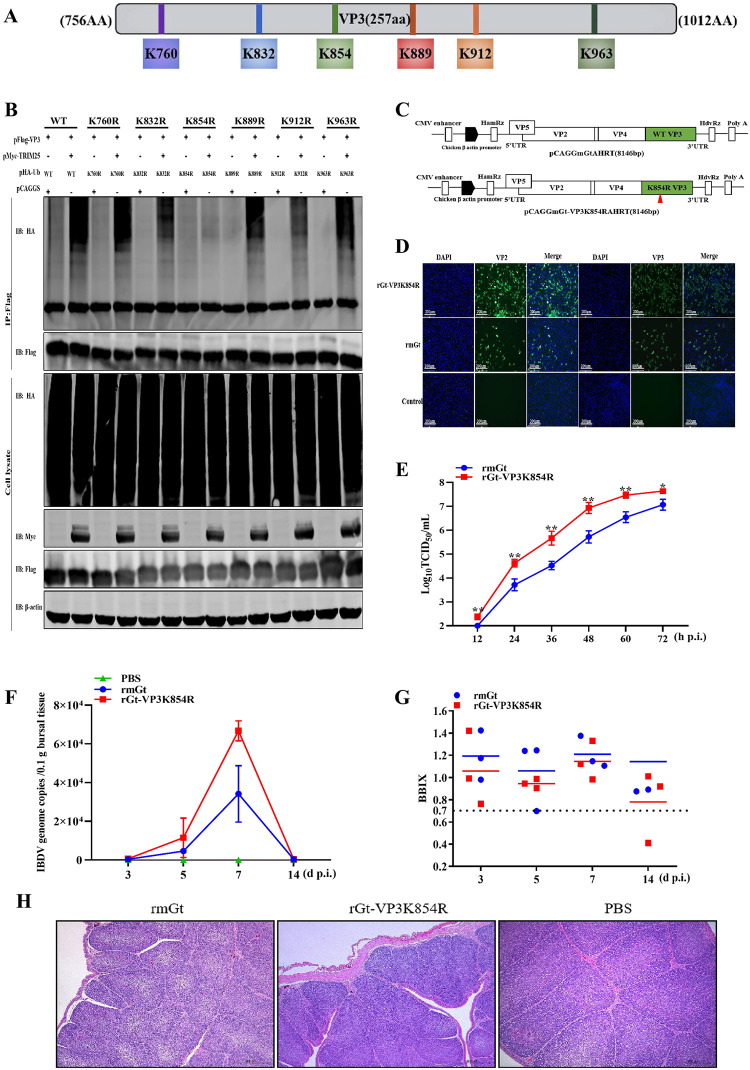
Fig 7. Lys854 of VP3 is a ubiquitination site of TRIM25.
(A) Schematic representation of the possible ubiquitination site of VP3. (B) The amino acid of VP3 was ubiquitinated by TRIM25. Different VP3 plasmids (WT and different mutants) and pHA-Ub were co-transfected with pMyc-TRIM25 for 36 h. Then, the lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (C) Schematic representation of the strategy of rescuing IBDV. Segments A and B were constructed according to the instruction in the Materials and methods section. (D) IFA assay. DF-1 cells were infected with rmGt and rGt-VP3K854R viruses and were detected with anti-VP2/VP3 mAb. (E) Replication activity between rmGt and rGt-VP3K854R was detected using a TCID50 assay in vitro. CEFs were infected with WT and mutant IBDV at the MOI of 0.01 for 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, and 72 h. The 3-week-old SPF chickens were challenged with 105.8TCID50/200 μL of two viruses, and bursae samples were collected at3, 5, 7, and 14 d p.i. (F) IBDV genome copies of rmGt and rGt-VP3K854R were detected by RT-qPCR in vivo. (G) BBIX of all challenged bursae. (H) Histopathological examination of bursae at 7 day p.c. Three independent experiments were performed, and data are shown as mean ± standard deviations for triplicates from a representative experiment. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.