Figure 5.
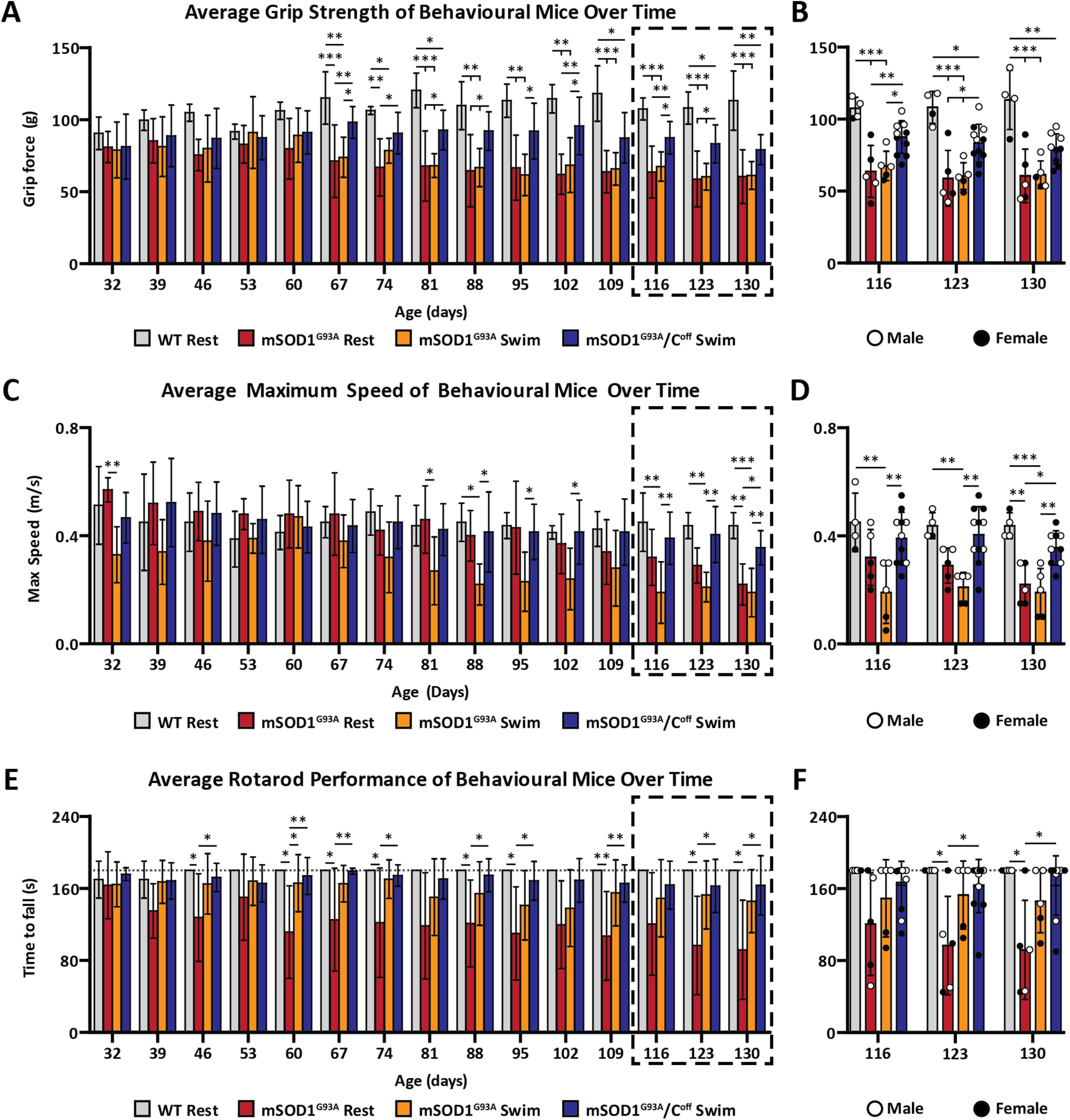
Training toward amplitude modulation in the absence of C-boutons significantly improves behavioral performance in mSOD1G93A mice. A, B, WT mice are significantly stronger than mSOD1G93A mice beginning at approximately P67 but are only significantly stronger than mSOD1G93A/Coff swim mice beginning at P109. mSOD1G93A/Coff mice also perform significantly better than their mSOD1G93A counterparts beginning at P67, though this difference is not present at P130. C, D, mSOD1G93A/Coff swim mice are significantly faster than their mSOD1G93A counterparts beginning at approximately P116 and never perform significantly worse than WT mice at all ages examined. E, F, mSOD1G93A/Coff swim mice outperformed the mSOD1G93A rest mice on the rotarod beginning at approximately P123. See Extended Data Figure 5-1 for data regarding qPCR results and swim performance. Bar graphs display the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
