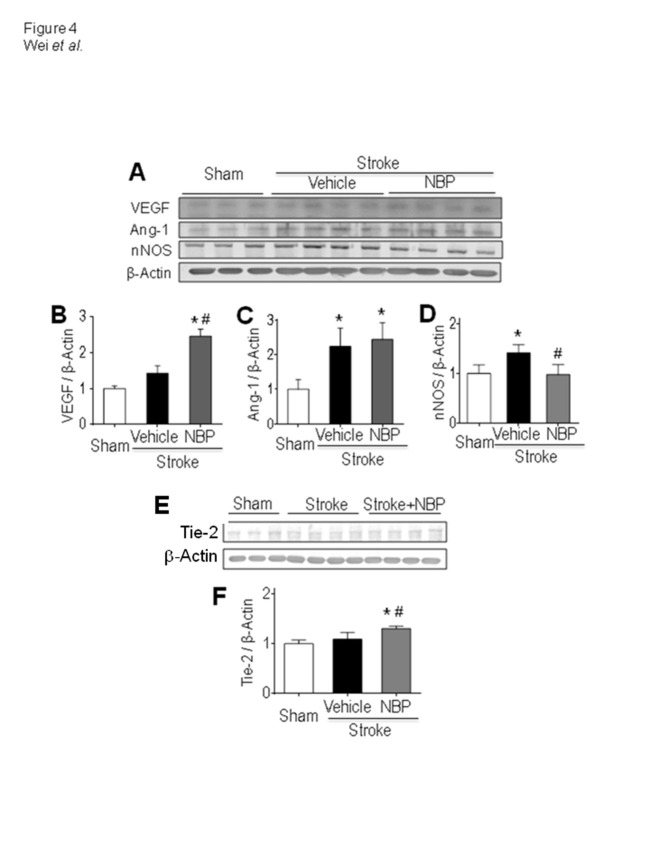
Figure 4.
Effects of NBP on neurovascular factors in the ischemic cortex. (A) The protein level of neurovascular regulatory factors VEGF, Ang-1, Tie-2 and nNOS in the peri-infarct region were detected by Western blot analysis 14 days after stroke. (B) Quantified data showed that, at this delayed time point, the VEGF level in the post-stroke brain was similar to that in sham controls while the NBP treatment significantly increased the VEGF expression. One-way ANOVA; F(2,8)=16.26, *p<0.05 vs. sham control, #p<0.05 vs. stroke+vehicle control, N=6 in sham group, N=8 in stroke and stroke plus NBP, respectively. (C) Stroke significantly enhanced the expression of Ang-1; there was no significant difference between stroke and stroke plus NBP group. One-way ANOVA; F(2,19)=19.07, *p<0.05 vs. sham, N=6 in sham group, N=8 in stroke vehicle and stroke plus NBP group, respectively. (D) The expression of nNOS in stroke vehicle animals increased compared to sham controls. Stroke animals received the NBP treatment, however, did not show similar increase. (E) and (F) The Tie-2 level was significantly increased by NBP. One-way ANOVA; F (2, 11) = 11.49; *p<0.05 vs. sham, #p<0.05 vs. stroke vehicle controls. N=6 in sham group, N=8 in stroke + vehicle group and stroke stroke + NBP group, respectively.