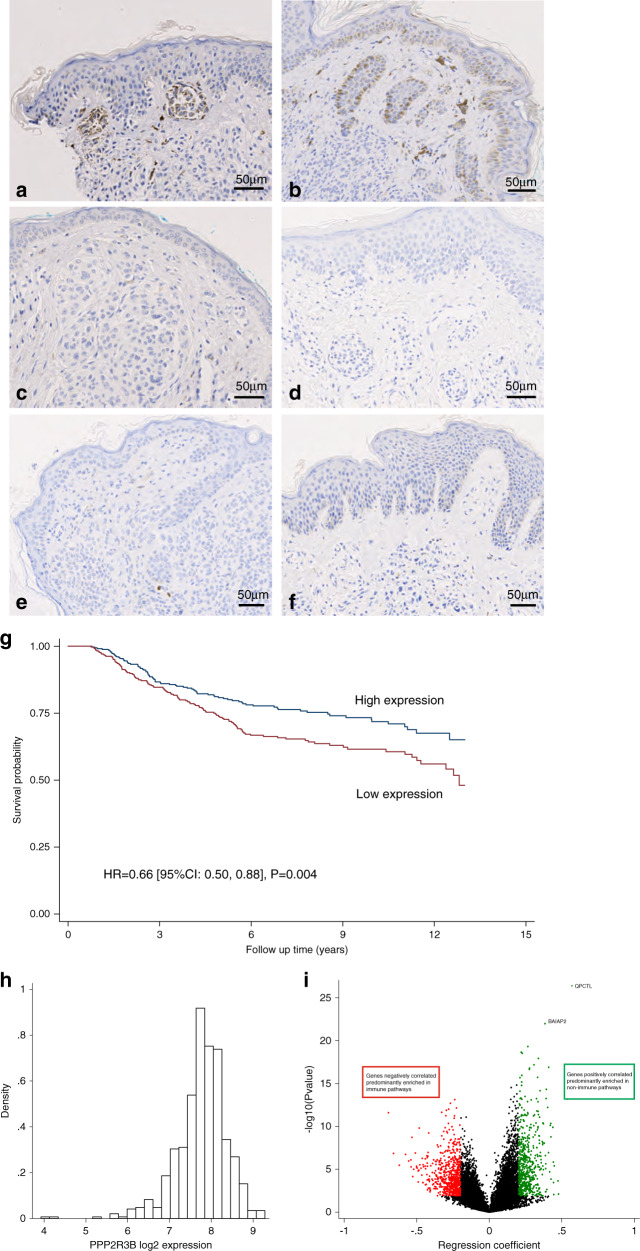
Fig. 2. Germline duplications of PPP2R3B lead to increased expression of protein product PR70 in congenital melanocytic nevi (CMN) tissue, compared to that of normal copy-number controls.
(a, b) Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) CMN tissue demonstrates moderate intensity PR70 staining throughout the cytoplasm of nevus cells in two patients where tissue was available with a confirmed germline PPP2R3B duplication and (c–f). Negative PR70 staining in four patients with confirmed normal copy number of PPP2R3B. Stained sections were assessed by two independent blinded assessors and assigned a score of 1–3, based on the intensity of staining observed and scores averaged. Scores were as follows: a = 3, b = 2.5, c = 0, d = 0, e = 0, and f = 0. Increased PPP2R3B expression in melanoma tissue is correlated with improved melanoma specific survival. (g) Kaplan–Meier curve generated from transcriptomic data from 703 FFPE melanoma tumors from the Leeds Melanoma Cohort, hazard ratio (HR) = 0.66, (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.50–0.88), p = 0.004. The effect remains significant after adjusting for age, sex, American Joint Committee for Cancer (AJCC) stage, vascular invasion, site, BRAF/NRAS pathogen variant status, and tumor invading lymphocytes (TILs). (h) Log intensity distribution of PPP2R3B DASL probe (ILMN_1689720) is close to a normal distribution. Improved melanoma specific survival observed with increased expression of PPP2R3B appears not to be immune mediated. Tumor expression of PPP2R3B correlates with expression of a large number of other genes in the genome: 596 positively correlated at FDR < 0.05 with regression coefficient >0.20; 731 negatively correlated at FDR < 0.05 with a regression coefficient < −0.2. (i) The genes positively correlated with PPP2R3B are predominantly enriched in nonimmune pathways, consistent with the lack of association between PPP2R3B expression and TILs or any specific immune cell score. The genes negatively correlated with PPP2R3B expression are predominantly enriched in immune pathways (Table S1, 2).