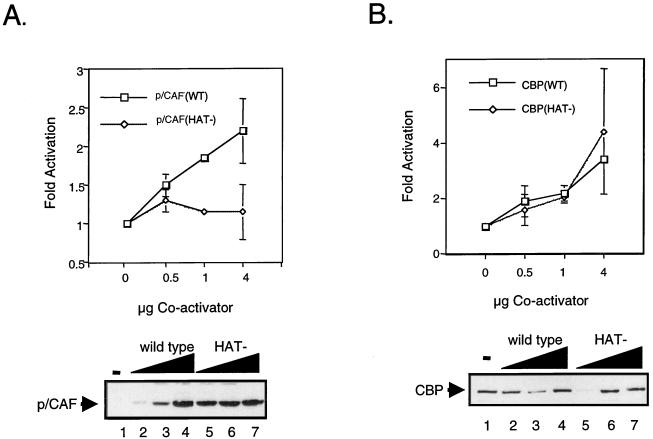
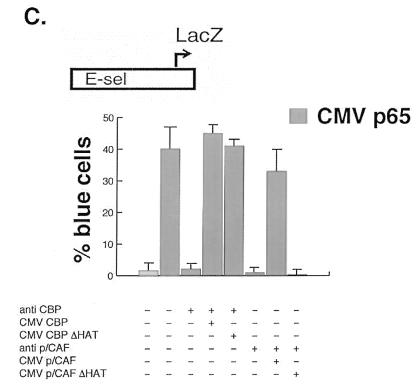
FIG. 6.
NF-κB-dependent transactivation in vitro requires p/CAF HAT activity. (A) The HAT activity of p/CAF is required for potentiation of p65-dependent transactivation (upper panel). COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with 1 μg of −578 E-selectin-CAT and 100 ng of pcDNA-p65 and 0.5, 1, or 4 μg of either wild-type (WT) CMV-p/CAF or CMV-p/CAF (HAT−). Forty-eight hours posttransfection, the cells were harvested and CAT activity was assayed as described in Materials and Methods. The level of activity observed upon cotransfection of E-selectin CAT and p65 was set at one. Data are presented as means; error bars, standard deviations. Representative Western blot analyses of wild-type p/CAF (lower panel, lanes 2 to 4) and HAT− p/CAF (lower panel, lanes 5 to 7) are shown. (B) The HAT activity of CBP/p300 is not required for potentiation of p65-dependent transactivation. COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with 1 μg of −578 E-selectin-CAT, 100 ng of pcDNA-p65, and 0.5, 1, or 4 μg of either wild-type (WT) RSV-CBP or CMV-CBP (HAT−). Forty-eight hours posttransfection, the cells were harvested and CAT activity was assayed as described in Materials and Methods. The level of activity observed upon cotransfection of E-selectin CAT and p65 was set at one. Data are presented as the means; error bars, standard deviations. Representative Western blots of wild-type CBP (lower panel, lanes 2 to 6) and HAT− CBP (lower panel, lanes 7 to 11) are shown. (C) HAT requirements for NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Plasmids consisting of a LacZ reporter under the transcriptional control of the E-selectin promoter were injected in the nuclei of Rat-1 cells in the presence of either an anti-CBP or an anti-p/CAF antibody. The expression of the reporter plasmid was monitored by X-Gal staining and quantitated based on the percentage of injected cells that stained blue. Rescue experiments were performed by coinjecting the indicated p/CAF or CBP expression plasmid.