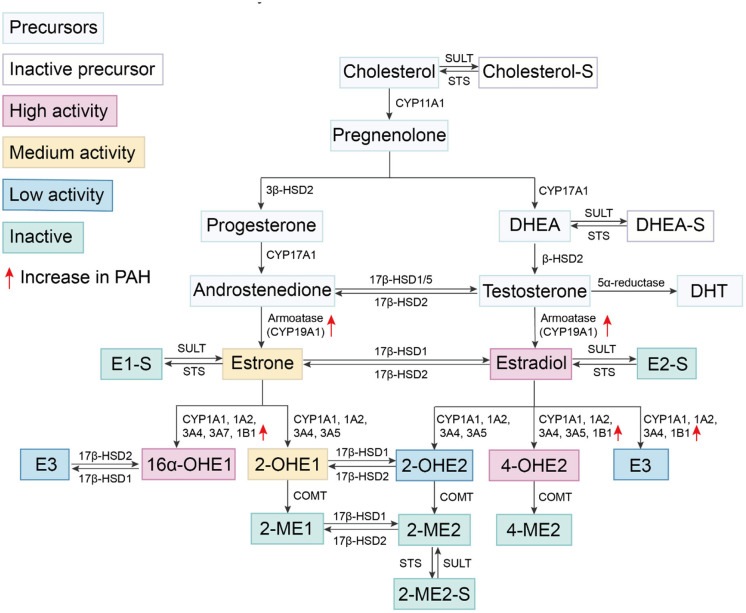
Figure 1.
Estrogen synthesis and metabolism. Cholesterol is catalyzed by the cytochrome P450 enzyme and undergoes several conversions to become DHEA. DHEA is converted to testosterone under the catalysis of different β-HSDs. Androstenedione and testosterone are converted into estrone and E2 by CYP19A1, respectively. E2 is oxidized on carbon at multiple positions, including oxidation at the C17 position by 17β-HSD responsible for the reversible conversion between E1 and E2. Other oxidation sites include those at C2, C4, and C16 positions and produce different metabolites via varying cytochrome P450 enzyme. E1, E2, estrogen precursors and some metabolites can be combined with sulfonate groups by SULT to convert them into sulfuric steroids. Sulfation of steroids can be converted into active forms by STS.