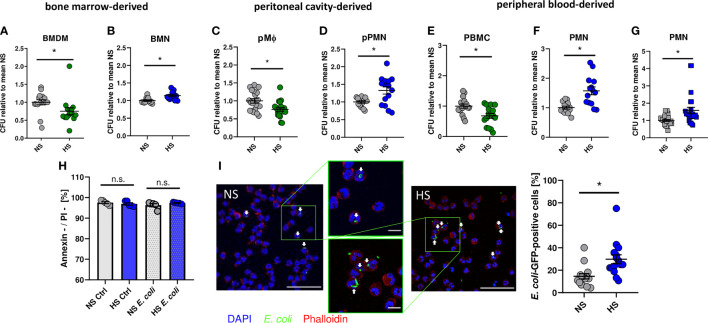
Figure 1.
High salt impairs bacterial killing of neutrophils. Antibacterial activity of (A) murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM; means ± s.e.m.; n = 15-16; Mann-Whitney test; *p < 0.05), (B) murine bone marrow-derived neutrophils (BMN; means ± s.e.m.; n = 12; Mann-Whitney test; *p < 0.05), (C) murine peritoneal macrophages (pMΦ; means ± s.e.m.; n = 20; Student’s t test; *p < 0.05), (D) murine peritoneal neutrophils (pPMN; means ± s.e.m.; n = 15; Student’s t test with Welch’s correction; *p < 0.05), (E) human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC; means ± s.e.m.; n = 16; Student’s t test; *p < 0.05) and (F) human peripheral blood neutrophils (PMN, means ± s.e.m.; n = 14; Student’s t test with Welch’s correction; *p < 0.05) infected with E. coli under NS or HS (NS + 40 mM NaCl) conditions. (G) Antibacterial activity of PMN infected with S. aureus (means ± s.e.m.; n = 24; Mann-Whitney test; *p < 0.05). (H) Cell viability by Annexin/PI staining in uninfected (Ctrl) and E.coli-infected PMNs (means ± s.e.m.; n = 5; Student’s t test and Mann-Whitney test; n.s., not significant; *p < 0.05). (I) Infection rate in PMN 1 h after E. coli-infection; Bacterial load under NS or HS conditions, intracellular bacteria marked by arrowheads. A representative image out of three independent experiments is displayed. E. coli-GFP, green; Phalloidin, red; DAPI (DNA), blue. Scale bar: 50 µm (means ± s.e.m.; n = 15; Mann-Whitney test; *p < 0.05).