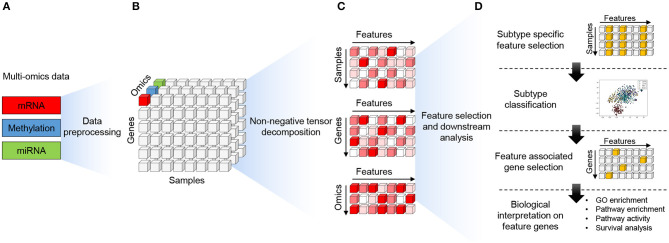
Figure 3.
The workflow of the MONTI framework. (A) Each omics data (gene expression, methylation, miRNA expression) is pre-processed as a two-dimensional gene-centric matrix comprised of genes and samples. (B) The omics matrices are then stacked to form a three-dimensional tensor structure (genes, samples, omics) all sharing the same genes and samples. (C) Using the PARAFAC approach, the tensor is decomposed into two-dimensional gene, patient and omics components. Here, the components share the rank features. (D) The patient component is used to select subtype-specific features using subtype-specific L1 classifiers. The selected subtype-specific features are used to build a subtype classifier model using MLP (Multi-layer perceptron). Genes associated to the subtype-specific features are then selected for biological function analysis.