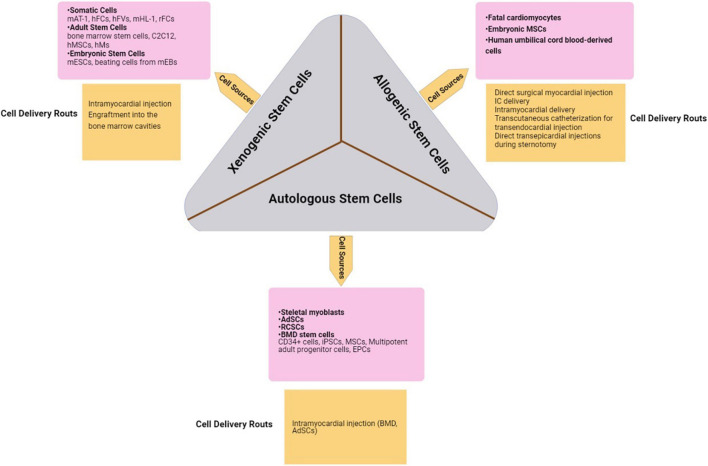
FIGURE 3.
Stem cells are collected from appropriate cell sources. The collected cells are replicated in suitable cultures in order to reduce the risk of tissue rejection. Finally, the generated tissues will be transported to the target organ via different tissue delivery routes due to their availability, invasiveness, and the target tissue’s characteristics (Xiao et al., 2004; Beeres et al., 2007a; Rodrigo et al., 2013; Alrefai et al., 2015; Henry et al., 2017; Konstanty-Kalandyk et al., 2018; Litwinowicz et al., 2018). hFCs, human fetal cardiomyocytes; hFVs, human ventricular cells; hMSCs, human mesenchymal stem cells; hMs, human myoblasts; mEBs, mouse embryoid bodies; mESC, mouse embryonic stem cells; rFCs, rat fetal cardiomyocytes; IC, intracoronary; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; AdSCs, adipose-derived stem cells; RCSCs, resident cardiac stem cells; BMD, bone marrow-derived stem cells; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells.