Figure 2.
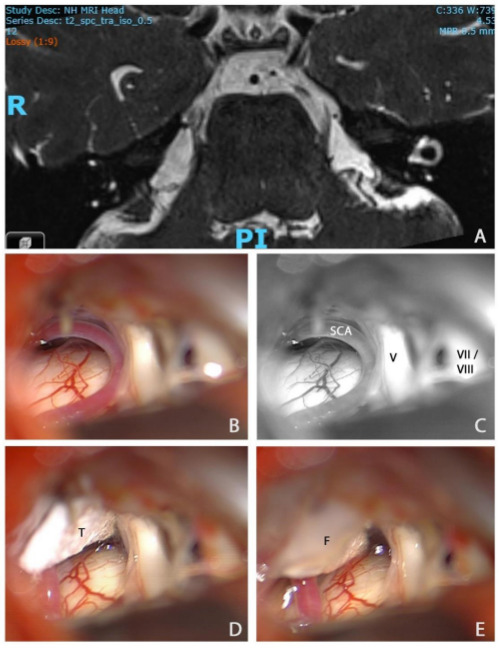
MR scan of the trigeminal nerve and intraoperative pictures during microvascular decompression in patient with classical trigeminal neuralgia. (A) Axial MR 0.5 mm volumetric SPACE sequence through the pons showing neurovascular conflict between the right superior cerebellar artery (SCA) and the right trigeminal nerve (V). (B) Intraoperative view of the right cerebellopontine angle, prior to right microvascular decompression, showing conflict between the right SCA and V. (C) Black and white rendition of the previous photograph with labelling of the superior cerebellar artery, V, and more superficial seventh and eighth nerve complex (VII/VIII). (D) The superior cerebellar artery has been mobilised and transposed superiorly towards the tentorium. It is held in place with a small piece of Teflon (T). (E) A small drop of fibrin glue (F) has been applied to ensure that the T does not migrate. A small ‘dent’ in the course of the trigeminal nerve can be seen at the site of the previous neurovascular conflict. SPACE, sampling perfection with application optimised contrasts using different flip angle evolution.
