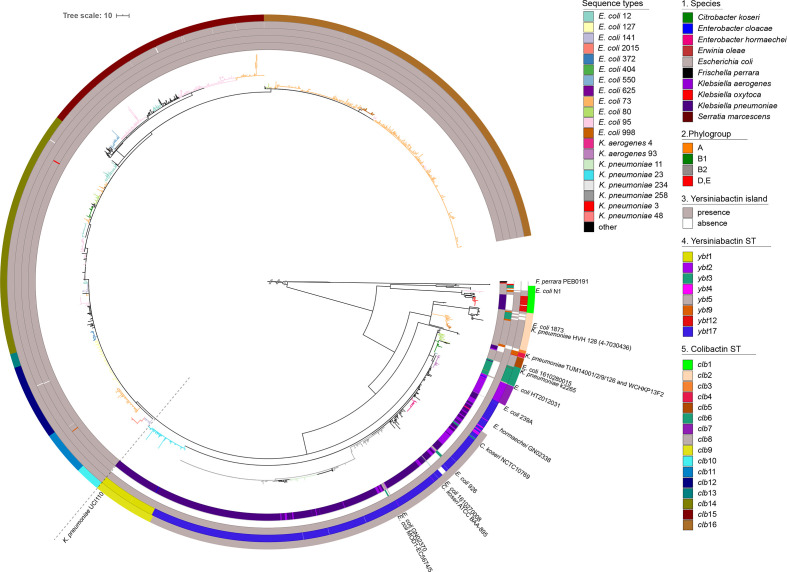
Fig. 3.
Maximum-likelihood-based phylogeny of the colibactin gene cluster detected in 2169 enterobacterial genomes. Every leaf represents a single sequence variant of the clb gene cluster, which can be allocated to different lineages and clades. From innermost to outermost, the first circle indicates the species harbouring the clb determinant; the second circle shows the Escherichia coli phylogroup, the third circle shows the presence/absence of the ybt operon; the fourth circle shows the yersiniabactin sequence types (YbST) of the ybt determinant (from Fig. 1b) that correspond to the pks island lineage present in the individual genome. The fifth circle shows the different colibactin sequence types (CbST) of the clb gene cluster. The branch colours in the centre of the tree depict the prominent bacterial sequence types (Fig. 1). The large conserved Escherichia coli phylogroup B2 clade is separated from the large Klebsiella clade with a faint broken line.