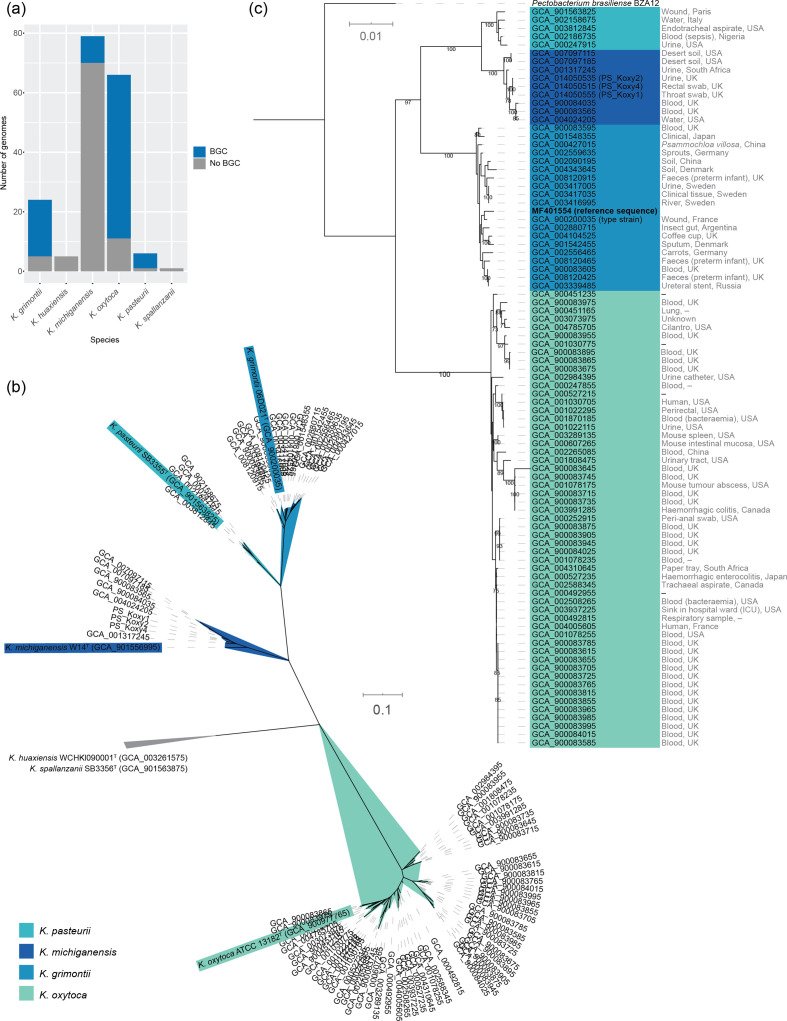
Fig. 3.
Distribution of the kleboxymycin BGC in Klebsiella spp. genomes. (a) Distribution of the K. oxytoca complex genomes encoding the entire kleboxymycin BGC. (b) Unrooted maximum-likelihood tree [generated using PhyloPhlAn v0.99 [34] and 380 protein-encoding sequences conserved across the genomes] confirming species affiliations of the 88 genomes within the K. oxytoca complex [1] encoding the kleboxymycin BGC. Type strains are shown with coloured backgrounds corresponding to the legend. The clade associated with K. huaxiensis and K. spallanzanii has been collapsed because of space constraints. (c) Maximum-likelihood tree generated with the concatenated protein sequences for the kleboxymycin BGC of the 88 genomes found to encode all 12 genes of the BGC plus the reference sequence [11]. The tree was rooted using the kleboxymycin-encoding BGC of Pectobacterium brasiliense BZA12. Values at nodes, bootstrap values expressed as a percentage of 100 replicates. Sources of isolates, where known, are shown to the right of the assembly accession numbers. (b, c) Scale bar, average number of substitutions per position.