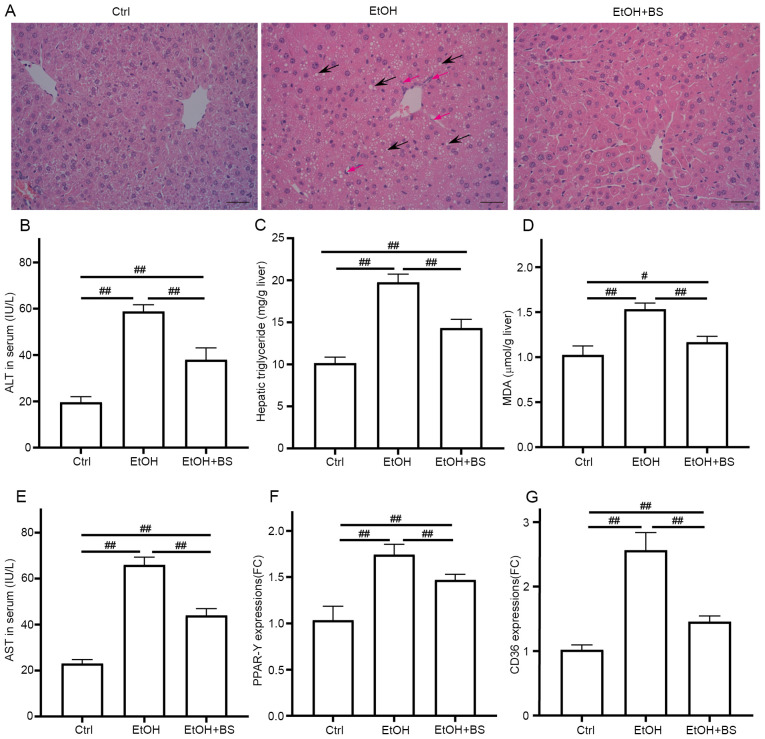
Figure 2.
BS supplementation alleviates alcohol-induced liver injury. (A) Representative photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin-stained liver sections, black arrows show the steatosis and red arrows show neutrophil infiltration (magnification, x200). (B) Serum ALT levels. (C) Hepatic triglyceride levels. (D) Hepatic TBARS levels. (E) Serum AST levels. (F and G) Hepatic expression of gene PPAR-γ and CD36, respectively. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. #P<0.05; ##P<0.01. BS, B. subtilis supplementation; ALT, alanine transaminase; TBARS, thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances; AST, aspartate transaminase; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; EtOH, ethyl alcohol; Ctrl, control; MDA, malondialdehyde.