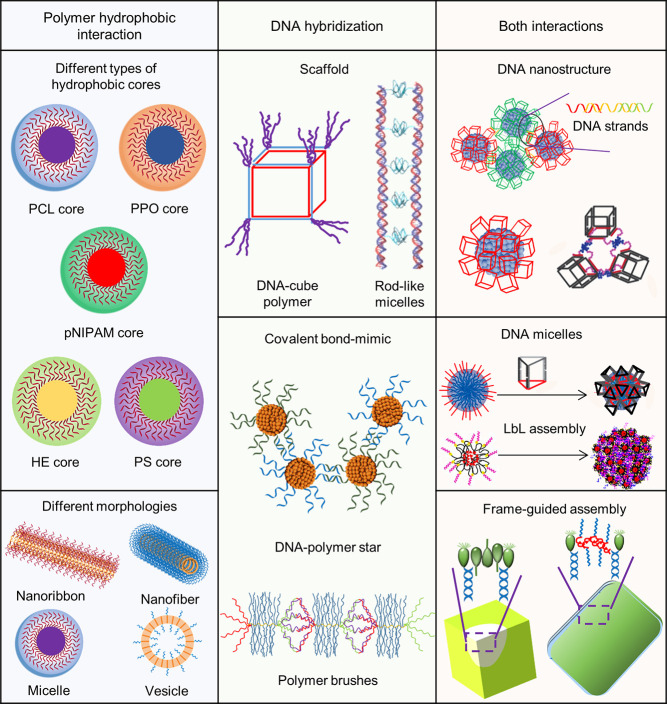
Figure 16.
Summary of DNA–polymer static nanostructures. The assembly methods are categorized as a hydrophobic polymer interaction, DNA hybridization, and both interactions. Through polymer hydrophobic interactions amphiphilic DNA–polymer can self-assemble into DNA nanostructures with various morphologies.172 Reproduced with permission from ref (172). Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society. When the long DNA templates are regarded as the rigid scaffolds, rodlike micelles can be formed by DNA hybridization.187 Reproduced with permission from ref (187). Copyright 2007 John Wiley and Sons. The assemblies of static DNA–polymer superstructures can form through both DNA hybridization and the polymer hydrophobic interactions to guide the assembly of DNA nanostructures–polymer hybrids.79,171 Reproduced with permission from ref (79). Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society. Reproduced with permission from ref (171). Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society.