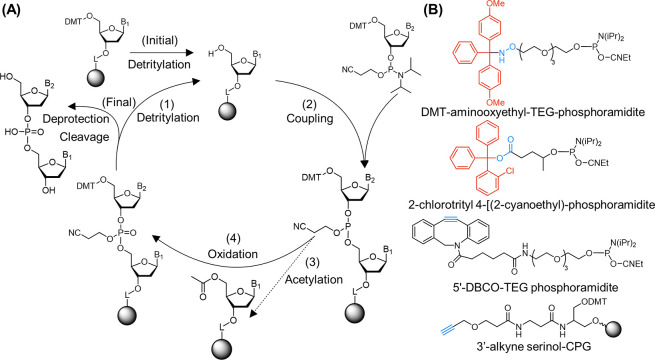
Figure 2.
(A) Solid phase synthesis of ODNs through automated phosphoramidite chemistry on a CPG bead. (1) An initial detritylation step is required to activate the primary nucleoside for coupling. (2) Once activated the protected nucleobase phosphoramidate is added for coupling to the 5′-hydroxy of the solid bound nucleoside. (3) Some of the coupling reactions may be unsuccessful; therefore, a capping step is included. Step (4) involves the oxidation of the phosphite to phosphate and completes one cycle. The addition of nucleotides can be continued by repeating step (1) to step (4) until the ODN sequence is complete. Once complete, a final deprotection and cleavage step is performed. (B) Functionalized phosphoramidites bearing chemical handles for column modification or downstream conjugation. Two examples of protecting groups, DMT and 2-chlorotrityl, are shown in red, and each functional group (aminooxy, carboxylic acid, and alkyne groups) is highlighted in blue.