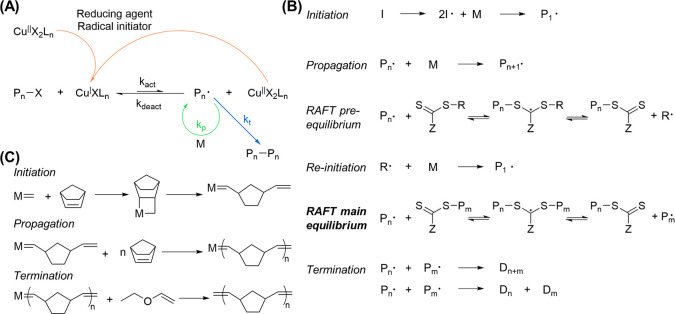
Figure 7.
Living polymerization techniques appropriate for DNA–polymer synthesis. (A) Schematic of Cu-catalyzed ATRP. The transition metal catalyst, here Cu, is reduced to activate and initiate the radical. Polymer propagation (Kp) occurs through radical polymerization of reactive monomers. Termination (kt) proceeds through the combination of reactive polymers. Catalysts are oxidized through the activation step and can deactivate either through the more prominent deactivation or by the reducing agent. The equilibrium between activated (kact) and deactivated (Kdeact) states is determined by the catalyst used. (B) RAFT polymerization mechanism where I = initiator, M = monomer, P = polymer, Z = radical stabilizing group, and D = dead polymer. (C) ROMP employing a metal catalyst for coordination to a strained alkene for olefin metathesis. Termination can be performed by the addition of ethyl vinyl ether to coordinate to and remove the metal catalyst.