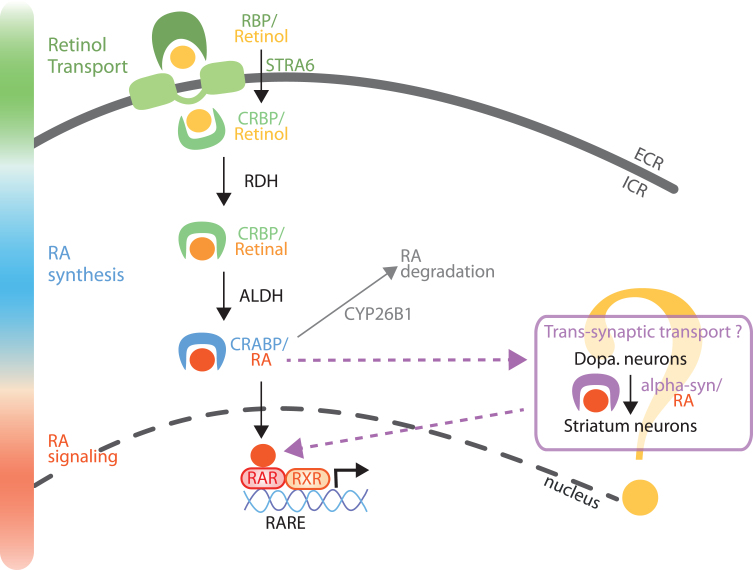
Fig. 2.
Model of RA metabolism and signaling in the nigro-striatal pathway. Retinol (vitamin A) is transported in the extracellular fluids by RBP, and internalized into the cells by STRA6. Retinol can also diffuse across the plasma membrane or through other transporters, not yet identified. Retinol is then bound to CRBP and metabolized into retinal by enzymes of the RDHs family. Retinal is further metabolized into RA by a RALDH protein (notably ALDH1A1 in a sub-population of SNc neurons). RA is then transported to the nucleus bound to CRABP protein. In the nucleus, RA binds to RA receptors (RARs), which activate the control of gene expression by RAR/RXR dimers on genes with a RARE sequence in their promoter. Furthermore, as a trans-synaptic factor, RA can travel trans-synaptically from SNc neurons to striatum neurons [24]. From the literature, it is possible that alpha-synuclein may serve as a cargo protein for the trans-synaptic transport of RA [26]. Finally, RA can be degraded by the Cyp26B1 enzyme. RBP, retinol binding proteins; STRA6, transporter stimulated by retinoic acid 6; CRBP, cellular retinol binding protein; CRABP, cellular retinoic acid binding protein; RDHs, retinol dehydrogenases; RALDHs, retinaldehyde dehydrogenases family (including ALDH1A1); RARE, retinoic acid receptor response element.