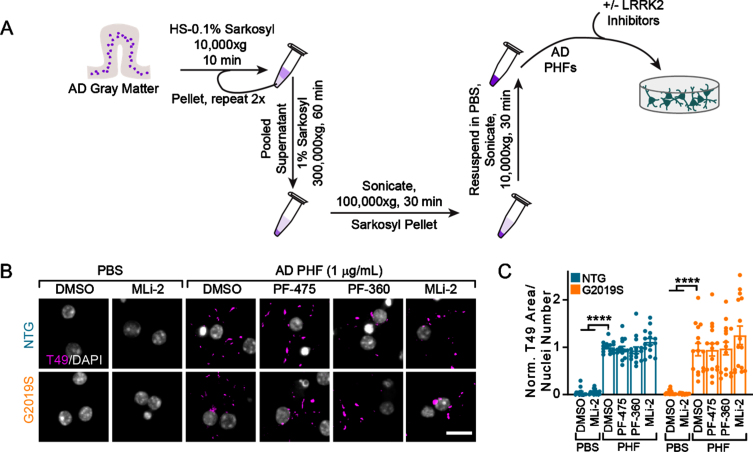
Fig. 3.
Tau from AD brains induces inhibitor-insensitive tau pathology in wildtype and LRRK2G2019S neurons. A) Schematic diagram of AD PHF tau extraction from human brain tissue and subsequent treatment of primary neurons. B) Primary hippocampal neurons from NTG or LRRK2G2019S mice were treated with vehicle or LRRK2 inhibitors at 300 nM at 5 DIV. They were further treated with AD PHF tau at 1μg/mL at 7 DIV, and both fixed and stained for insoluble mouse tau (T49, magenta) and DAPI (gray) at 21 DIV. Scale bar = 15μm. C) Quantification of the insoluble mouse tau area/nuclei number in each condition. No insoluble tau was present in the absence of PHF treatment and there was no overall effect of genotype (Two-way ANOVA; genotype effect p = 0.837, Dunnett’s multiple comparison test within genotype: NTG: DMSO-PHF vs. DMSO ****p < 0.0001; DMSO-PHF vs. MLi-2 ****p < 0.0001; G2019S:: DMSO-PHF vs. DMSO ****p < 0.0001; DMSO-PHF vs. MLi-2 ****p < 0.0001; all other values were not statistically significant, n (separate cultures) = 15 independent samples/group). Data are represented as mean±SEM with individual data points plotted.