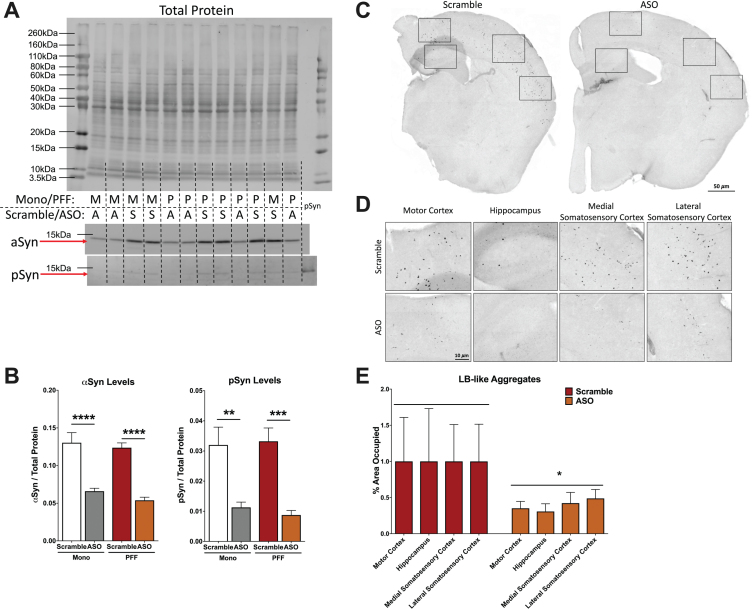
Fig. 2.
Analysis of α-synuclein (αsyn) and phosphorylated synuclein (psyn) protein levels in the hippocampus and LB-like pathology. A) Representative blot of total protein stain (top), αsyn band at 14.4 kDa (middle) and psy band at 14.4 kDa (bottom). Lanes are indicated with “M” for Mono, “P” for PFF, “A” for ASO, and “S” for scramble. The far right lane (lane 14) is a psyn positive control. B) Left: Quantification of αsyn, normalized to total protein. A two-way ANOVA indicated a main effect of ASO treatment (F(1,29) = 74.33, p < 0.0001) and Sidak’s post-hoc tests indicated αsyn protein was decreased in Mono-ASO mice compared to Mono-Scramble (p < 0.0001) and PFF-ASO compared to PFF-Scramble (p < 0.0001). Right: Quantification of psyn, normalized to total protein levels. A two-way ANOVA indicated a main effect of ASO treatment (F(1,29) = 35.88, p < 0.0001) and Sidak’s post-hoc tests indicated psyn protein was decreased in Mono-ASO mice compared to Mono-Scramble (p < 0.01) and PFF-ASO compared to PFF-Scramble (p < 0.001). Data presented as group averages±SEM. C) Representative images from mice injected with PFF-Scramble (left) and PFF-ASO (right). D) Higher magnification representative images of the motor cortex, hippocampus, medial somatosensory cortex, and lateral somatosensory cortex from the hemispheres in (C). PFF-Scramble is on the top, PFF-ASO is on the bottom. E) Normalized percent area occupied of LB-like aggregates in the motor cortex, hippocampus, lateral somatosensory cortex, and medial somatosensory cortex. Comparison of Scramble vs. ASO revealed an overall decrease in LB-like burden (t(65) = 2.280, p < 0.05), but pathology in individual brain regions was not significantly reduced. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.