Figure 8.
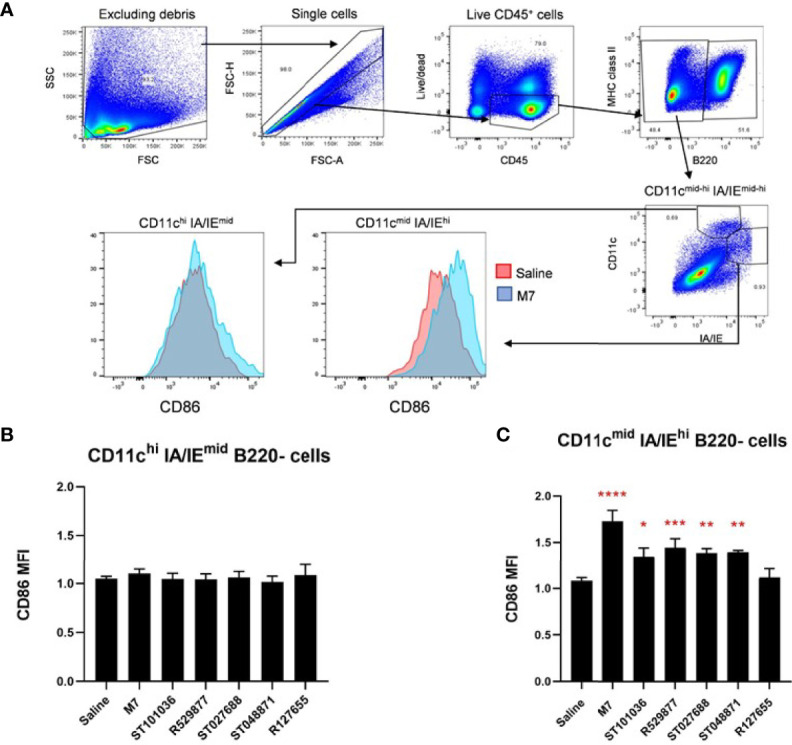
Mast cell activators enhance co-stimulatory molecules on dendritic cells in the draining cervical lymph nodes. Mouse resident and migratory dendritic cells in the draining cervical lymph node were monitored for CD86 expression after exposure to 200 nmoles of the mast cell activating compounds (ST101036, R127655, R529877, ST027688, ST048871), M7 (positive control), or saline (negative control). The gating strategy used to identify the cell populations is presented in (A). Resident DCs are characterized as CD11chi and MHCIImid (B) and Migratory DCs are characterized as CD11cmid and MHCIIhi populations (C). Compound-induced CD86 expression is normalized to DCs from mice exposed to saline. One-way ANOVA determined a significant increase compared to saline *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Bars represent the mean + SEM. MFI denotes mean fluorescence intensity.
