Fig. 2.
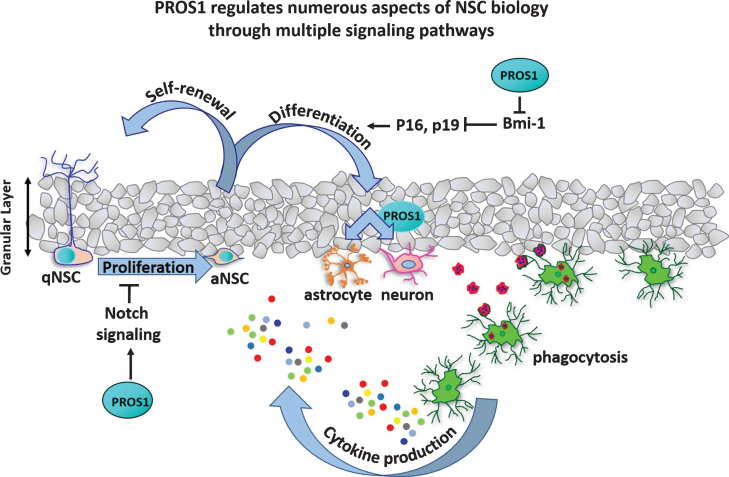
PROS1 regulates numerous aspects of NSC biology through multiple signaling pathways. Schematic of the dentate gyrus granular layer, indicating the influence of PROS1 on different phases of adult NSCs and neurogenesis. Quiescent NSCs (qNSCs) are glia-like and present with a dendritic arbor spanning the granular layer. Quiescent NSCs express PROS1, considered a stem-cell maintenance factor. PROS1 regulates Notch1 signaling, and suppresses NSC proliferation [25]. Upon integration of various signals, qNSCs begin to amplify through proliferation. Amplifying NSCs (aNSCs) also express PROS1, which promotes NSC differentiation by inhibiting Bmi-1, a transcriptional repressor of p16 and p19 which allows for continuation of self-renewing cell divisions [24]. PROS1 expression in differentiated NSCs promotes a neural cell fate over astrogenesis [25]. Within the neurogenic niche, PROS1 is highly expressed by microglia, where it is thought to regulate cytokine expression and phagocytosis of apoptotic neurons, thus influencing neurogenesis in a non-cell autonomous manner.