Figure 2.
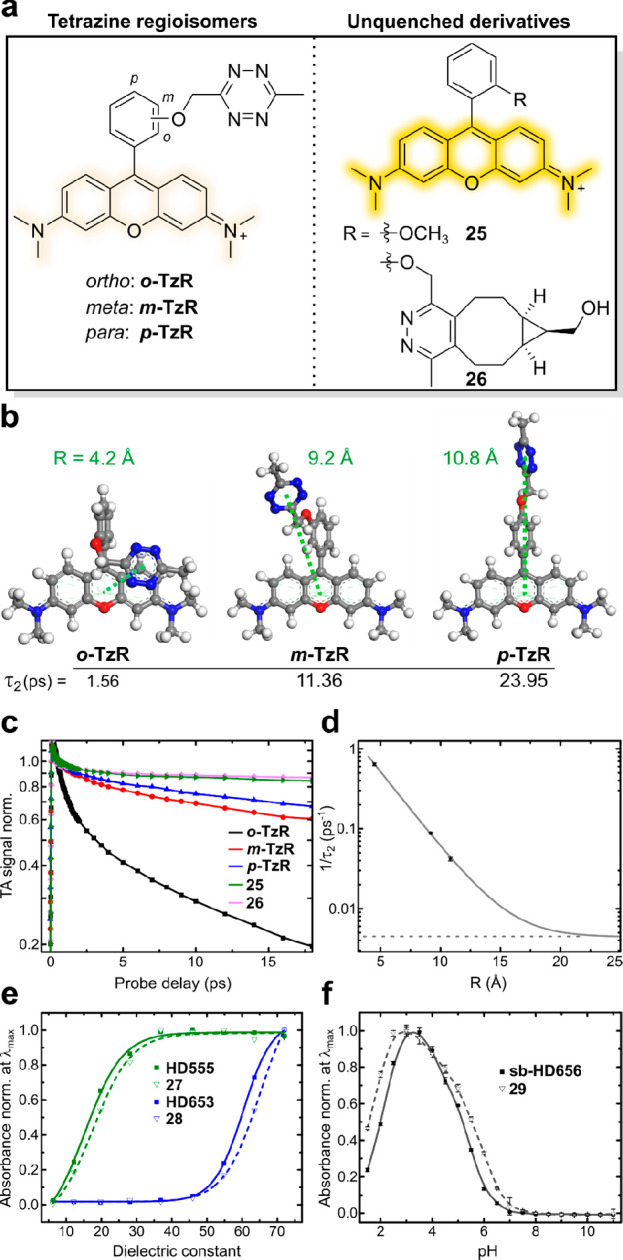
Fluorescence quenching and physicochemical properties of HDyes. (a–d) Time-resolved spectroscopy to study fluorescence quenching: (a) Structures of tetrazine rhodamine regioisomers and unquenched reference dyes. (b) DFT-optimized structures of o/m/p-TzR, respective tetrazine–xanthene intramolecular distances (R), and transient absorption decay times τ2. (c) Selected transient absorption traces at 560 nm (max. of GSB/SE). Data was normalized at a probe delay of 0.5 ps to avoid contributions of the coherence spike and vibration coherence at earlier delay times. (d) Experimental decay rates (1/τ2) obtained from global fitting of the transient absorption data and its dependence on R. Single-exponential fitting was performed assuming a constant offset (dashed horizontal line) obtained from the average lifetimes τ2 (see Table S3) of nonquenched derivatives 25 and 26. (e,f) Solvatochromic spirocyclization properties: (e) Normalized absorbance at λmax (zwitterionic form) of 7-CO2H tetrazine dyes and respective cycloadducts as a function of the dielectric constant of water/dioxane mixtures (v/v; 10/90 to 90/10). (f) Normalized absorbance at λmax (measured in triplicates) of 7-CH2OH tetrazine dye sb-HD656 and respective cycloadduct 29 as a function of pH.
