Figure 6.
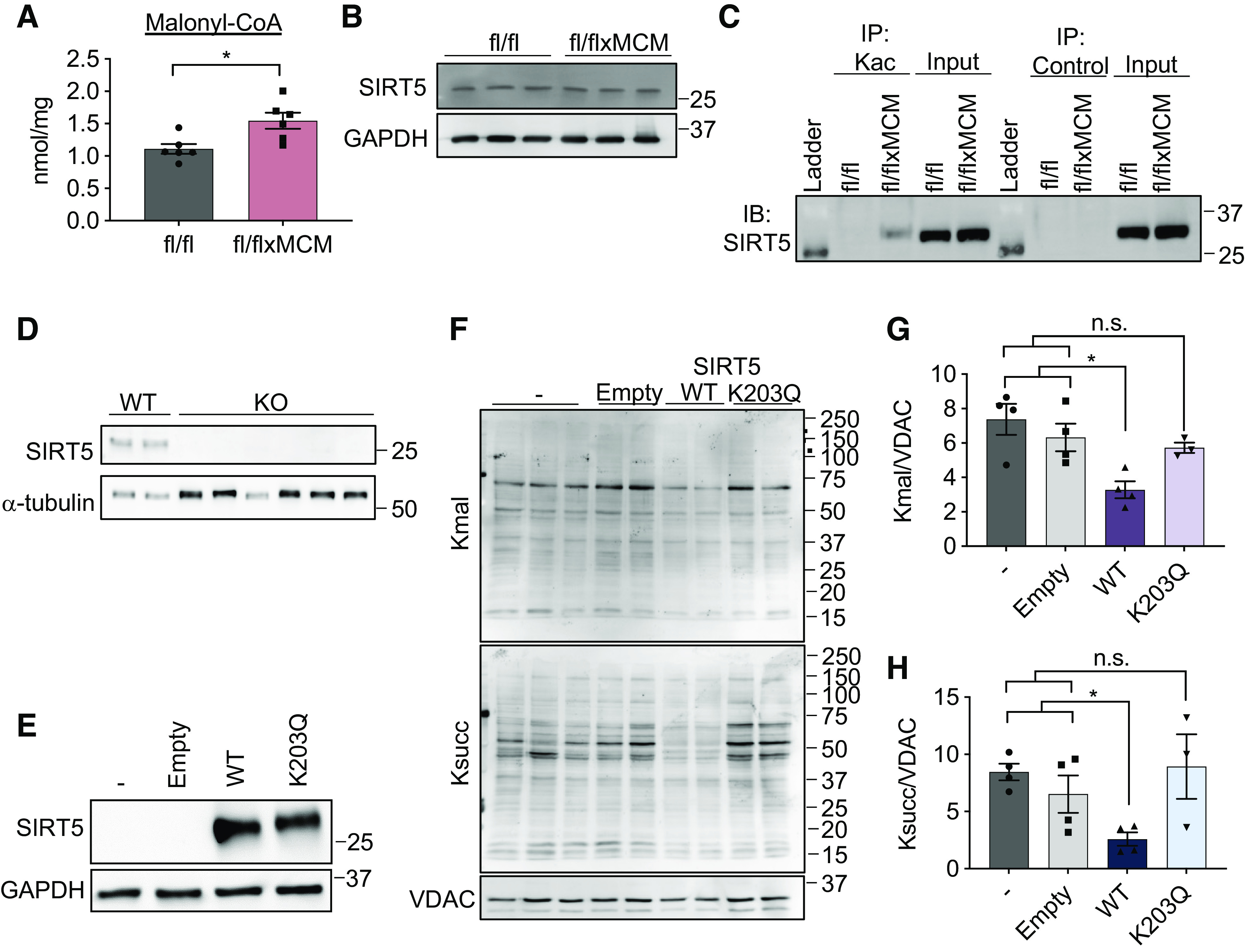
Acetylation of sirtuin 5 (SIRT5) modulates malonylation status of mitochondrial proteins. A: cardiac malonyl-CoA levels in Slc25a3fl/fl vs. Slc25a3fl/flxMCM mice at 10 wk post-tamoxifen administration (n = 5 fl/fl and n = 6 fl/flxMCM animals). B: Western blot analysis of SIRT5 expression in total heart protein lysates from Slc25a3fl/fl vs. Slc25a3fl/flxMCM animals. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C: immunoprecipitation confirmation of enhanced SIRT5 acetylation in Slc25a3fl/flxMCM vs. Slc25a3fl/fl hearts. Acetylated proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Kac antibodies followed by immunoblotting with an antibody against SIRT5. An anti-HA antibody was used as an immunoprecipitation control. D: Western blot analysis of SIRT5 expression in HEK293 WT vs. SIRT5 KO clones. α-Tubulin was used as a protein loading control. E: Western blot analysis of SIRT5 expression in SIRT5 KO cells reexpressing a pcDNA3.1 empty vector, WT SIRT5, or the SIRT5 K203Q mutant. GAPDH was used as a loading control. F: representative Western blot of protein lysine malonylation (Kmal) and succinylation (Ksucc) of mitochondria isolated from SIRT5 KO cells, or SIRT5 KO cells reexpressing the empty vector, WT SIRT5, or SIRT5 K203Q. VDAC was used as a loading control. G: quantification of protein malonylation in SIRT5 KO cells reexpressing the wild-type (WT) and K203Q SIRT5 constructs (n = 3–4 replicates/group). H: quantification of protein succinylation in SIRT5 KO cells reexpressing the WT and K203Q SIRT5 constructs (n = 3–4 replicates/group). One-way ANOVA followed by Welch’s test was used for statistical analysis with P < 0.05 considered significant. *P < 0.05, n.s., not significant.
