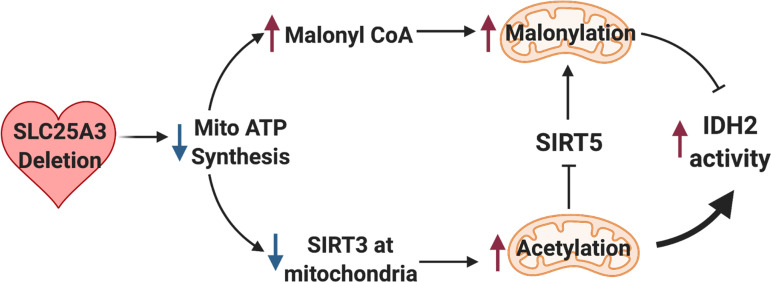
Figure 7.
Model of mitochondrial energy dysfunction-induced enhancement of mitochondrial protein acylation. Deletion of SLC25A3 deletion in the heart causes impaired mitochondrial ATP synthesis resulting in mitochondrial energy dysfunction. This leads to mitochondrial protein hyperacetylation and hypermalonylation. Loss of SLC25A3 decreases sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) in cardiac mitochondria, which can lead to increases in mitochondrial protein acetylation. Loss of SLC25A3 also increases cardiac malonyl-CoA levels, which can support enhanced malonylation. In addition, SLC25A3 deletion results in SIRT5 acetylation, which inhibits SIRT5 function as a second mechanism to potentiate mitochondrial malonylation. Finally, while mitochondrial energy dysfunction-induced malonylation decreases IDH2 activity, acetylation increases IDH2 activity. The cumulative effect of mitochondrial energy dysfunction-induced acetylation and malonylation of IDH2 increases IDH2 activity. Created using BioRender.com.