Figure 3. Inositol binds to AMPK and regulates AMPK activity and mitochondrial fission.
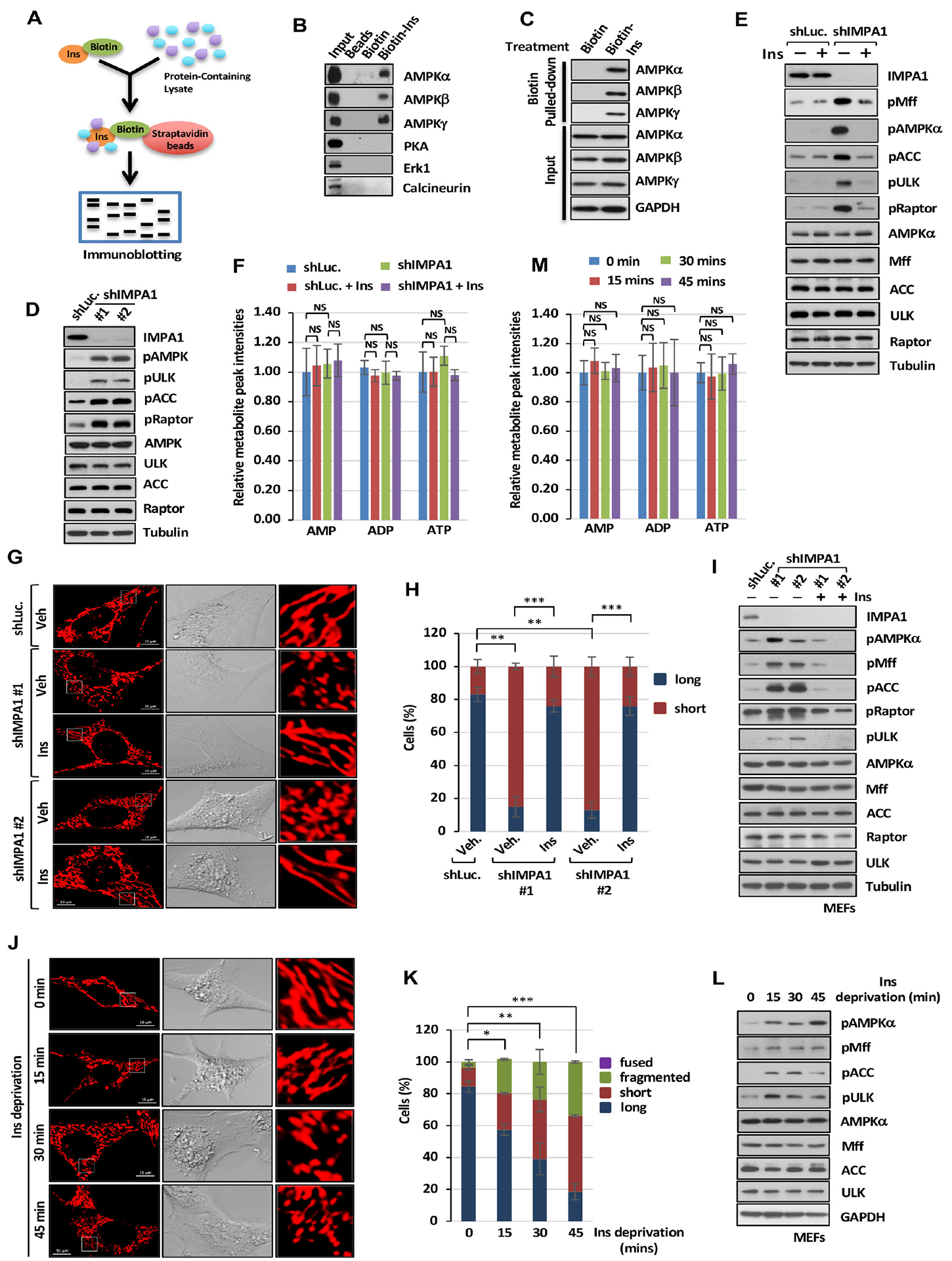
(A) Biotin-labeled inositol (Biotin-Ins) in vitro binding assay was performed by immunoblotting analysis. (B) Immunoblotting of biotin pull-down assay in PC3 cells with indicated antibodies. (C) Immunoblotting of biotin pull-down assay upon 25 μM of biotin or Biotin-Ins treatment for 1 hour. (D) Immunoblotting of shLuc. or shIMPA1 PC3 cells. (E) Immunoblotting with of shLuc. or shIMPA1 PC3 cells upon vehicle or Ins treatment. (F) Metabolic profiling of AMP, ADP and ATP in DU145 cells expressing shLuc. or shIMPA1 upon vehicle (Veh) or Ins treatment was performed by targeted mass spectrometry analysis. (G) Confocal images of mitochondrial morphology in shLuc. or shIMPA1 MEFs upon Veh. or Ins treatment. Scale bar, 10 μm. (H) Quantification of the mitochondrial morphology of the MEFs shown in (G). (I) Immunoblotting of shLuc. or shIMPA1 MEFs upon Veh. or Ins treatment. (J) Confocal images of mitochondrial morphology in MEFs upon Ins deprivation. Scale bar, 10 μm. (K) Quantification of the mitochondrial morphology of the cells shown in (J) upon Ins deprivation. (L) Immunoblotting of MEFs upon Ins deprivation. (M) Metabolic profiling of AMP, ADP and ATP in MEFs upon inositol deprivation was performed.
