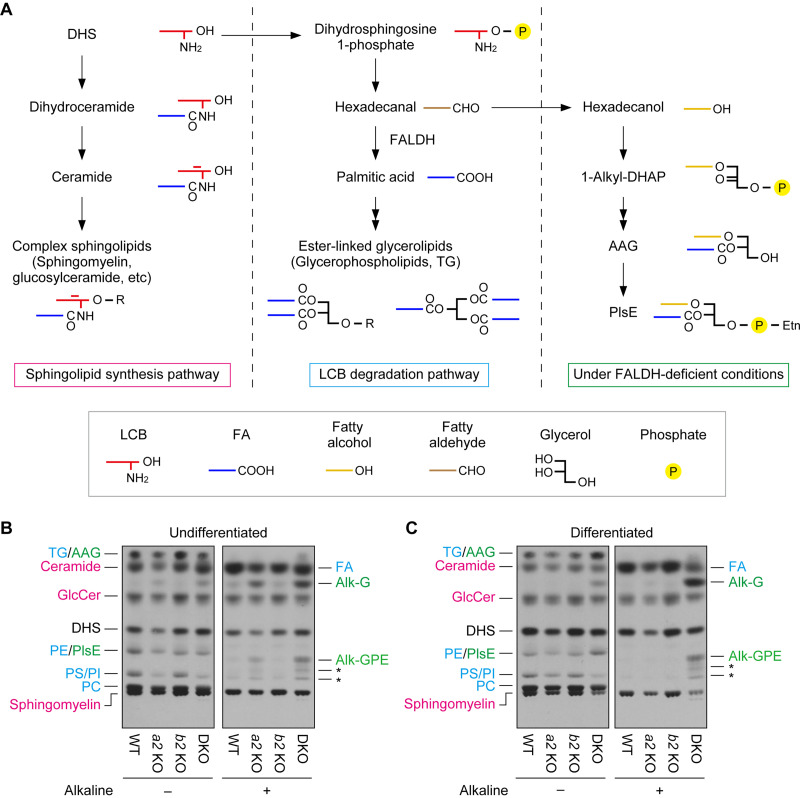
FIG 9.
Impaired long-chain base (LCB) metabolism in Aldh3a2 Aldh3b2 DKO mouse keratinocytes. (A) Metabolism of dihydrosphingosine (DHS) is illustrated. Under normal conditions, DHS is metabolized to complex sphingolipids in the sphingolipid synthesis pathway (left) or to ester-linked glycerolipids in the degradation pathway (middle). However, under FALDH-deficient conditions, such as ALDH3A2 mutation in humans and Aldh3a2 Aldh3b2 DKO in mice (right), the conversion of DHS to ester-linked glycerolipids is impaired, and DHS is instead metabolized to ether-linked glycerolipids. The simplified structure of each lipid is also shown. AAG, 1-alkyl/alkenyl-2-acyl-glycerol; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; PlsE, plasmanyl/plasmenyl phosphatidylethanolamine; R, polar head group. (B and C) Primary keratinocytes were prepared from WT, Aldh3a2 KO, Aldh3b2 KO, and DKO mice, and undifferentiated (B) and differentiated (C) keratinocytes were labeled with [3H]DHS at 37°C for 4 h. Lipids were extracted, given alkaline treatment or left untreated, separated via TLC, and detected using autoradiography. Asterisks indicate unidentified products of PlsE resulting from alkaline treatment. The colors represent lipids generated via the sphingolipid synthesis pathway (magenta) or the LCB degradation pathway under normal conditions (blue) or FALDH-deficient conditions (green). Alk-G, 1-alkyl/alkenyl-glycerol; Alk-GPE, 1-alkyl/alkenyl-glycerophosphoethanolamine; GlcCer, glucosylceramide; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PS, phosphatidylserine; a2 KO, Aldh3a2 KO; b2 KO, Aldh3b2 KO.