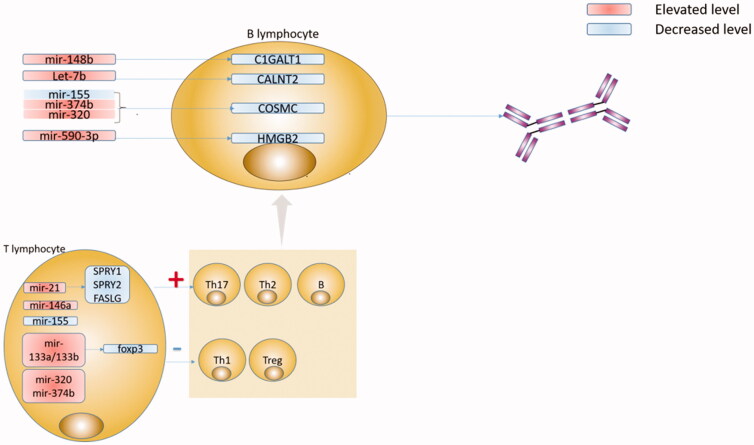
Figure 1.
Specific microRNAs (miRNA), their putative targets, and pathophysiological effects in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). A number of steps in the pathogenesis of IgAN are regulated by miRNA: upregulated miR-148b inhibits C1GALT1, upregulated let-7b inhibits CALNT2, upregulated miR-374b, miR-320, and downregulated miR-155 inhibits COSMC in B lymphocyte. These enzymes had been demonstrated important roles in the molecular basis for the aberrant IgA1 glycosylation in IgAN. Meanwhile, upregulated miR-590-3p inhibits HMGB2 in B lymphocytes, and the mechanism HMGB2 affects the production of gd-IgA1 remains unclear and needs further research. The immunoregulatory disorder is another important mechanism in IgAN. In T lymphocyte, upregulated miR-21 inhibits SPRY1, SPRY2 and FASLG, upregulated miR-133a/133b inhibits foxp3, and upregulated miR-146a, miR-320, miR-374b, and downregulated miR-155 induces Th17 polarization and influence the fitness of Treg cells and the Th1/Th2 balance.