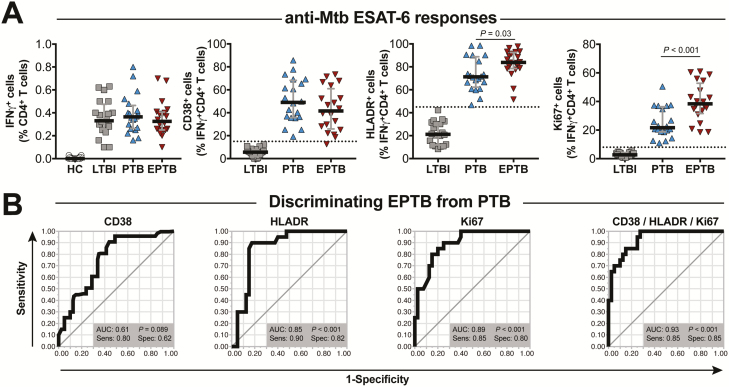
Figure 2.
In individuals without human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), EPTB can be distinguished from PTB based on frequencies of IFN-γ +CD4+ T-cell lymphocytes expressing HLADR+ and Ki67+. A, Frequencies of total IFN-γ +CD4+ T cells as well as of CD38+, HLADR+, and Ki67+ cells within IFN-γ + CD4+ T-lymphocytes from peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with ESAT6-CFP10 peptide pools (10 µg/mL) obtained from HIV-unexposed healthy controls (n = 20), LTBI (n = 50), EPTB (n = 50), or PTB patients (n = 50). Lines represent median values and interquartile ranges. Data from EPTB and PTB were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test. B, Receiver operator characteristic curve analyses of frequencies of CD38+, HLADR+, and Ki67+ and when all parameters were considered simultaneously to distinguish EPTB and PTB patients. Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; EPTB, extrapulmonary tuberculosis; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; LTBI, latent tuberculosis infection; Mtb, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; PTB, pulmonary tuberculosis; Sens, sensitivity; Spec, specificity.