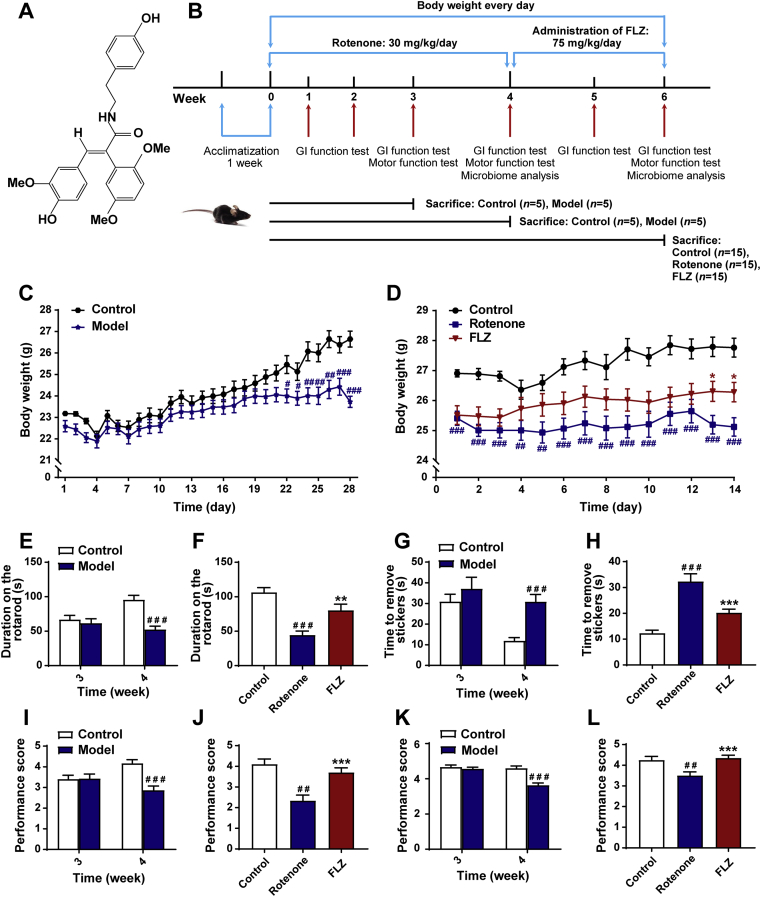
Figure 1.
FLZ treatment alleviates weight loss and motor dysfunctions of the rotenone-induced PD mice. (A) The chemical structure of FLZ. (B) The flow chart of animal treatments. (C) The body weight of mice from Weeks 1–4 (n = 15 for Control group; n = 30 for Model group). (D) The body weight of mice from Weeks 5–6 (n = 15 for each group). (E)–(F) Rotarod tests in Weeks 3–4 (E) and Week 6 (F). (G)–(H) Adhesive removal tests in Weeks 3–4 (G) and Week 6 (H). (I)–(J) Hanging grip test in Weeks 3–4 (I) and Week 6 (J). (K)–(L) Pole test scores in Weeks 3–4 (K) and Week 6 (L). For behavioral tests in Weeks 3–4, n = 15 for the Control group; n = 30 for the Model group. For behavioral tests in Weeks 5–6, n = 15 for each group. Data are presented as mean ± SD. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 versus the Control group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus the Rotenone group.