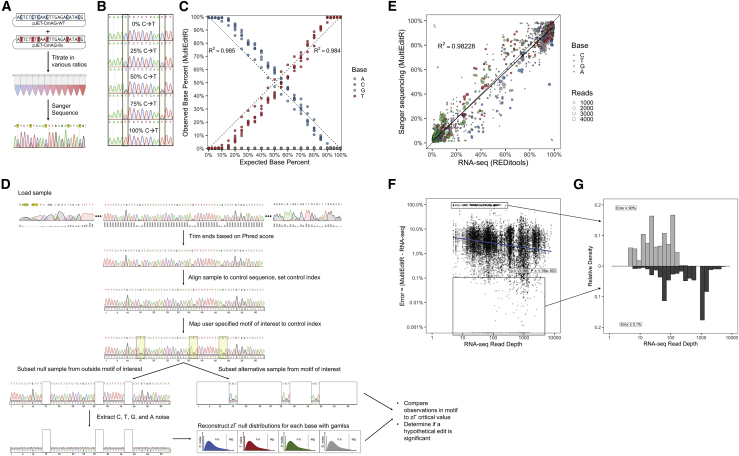
Figure 1.
Development and initial assessment of MultiEditR
(A) Experimental scheme for the plasmid titration experiment. (B) Representative chromatograms from C-to-T titration experiment showing a change in peak height at two sites. (C) Titration of pJET-CmAG-WT with pJET-CmAG-6x sequenced with the reverse primer; the coefficient of determination (R2) was calculated relative to the identity line. n = 6 editing sites per chromatogram. (D) Diagram of MultiEditR algorithm showing end trimming, sample alignment, motif mapping, zero adjusted gamma (zΓ) distribution generation, and null hypothesis significance testing. The MultiEditR algorithm can be applied to any motifs, WT base, and edited base identity. (E) Scatterplot of measurements of editing from Sanger sequencing by MultiEditR against measurements of editing from RNA-seq by REDItools. Coefficient of determination (R2) represents regression to the identity line. The overlaid black line is the linear model of best fit. Dot size is proportional to RNA-seq read coverage at the base of interest. (F) Absolute value of error in MultiEditR measurements by RNA-seq read depth. Population at the top of the graph with low read depth represents bases with >90% error in measurements. Data were analyzed by Spearman’s rank-order correlation test. (G) Mirrored histogram showing populations with high (≥90%) error and low (≤0.1%) error in MultiEditR measurements as a function of RNA-seq read depth.